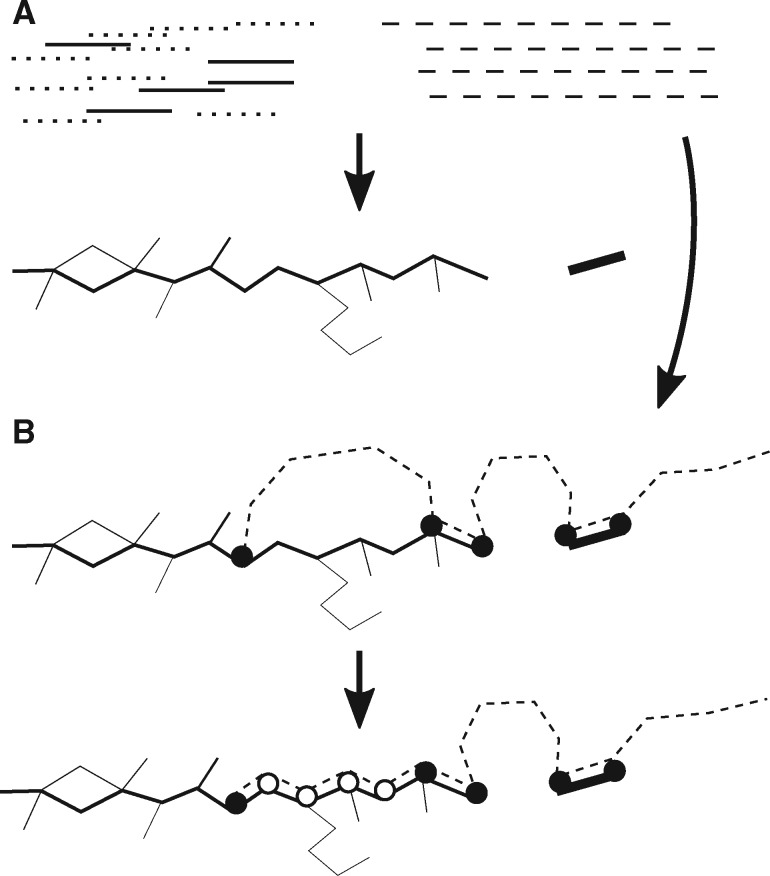
Fig. 1.
Simplified VAPOR algorithm. Firstly, pre-processing and graph construction is performed (A), where target reads R (solid black lines) are filtered from non-target (e.g. bacterial) reads (dotted lines) using a fast k-mer comparison to references S. This is followed by wDBG construction. Then, mapping and scoring is performed simultaneously (B), where each reference sequence s (dashed line) is mapped to the wDBG, , built from these reads. This is done in two main steps: exact k-mer matching (black circles) and extension (white circles) by heuristic graph traversal