Fig. 1. Crotonic acids decrease p53 protein level.
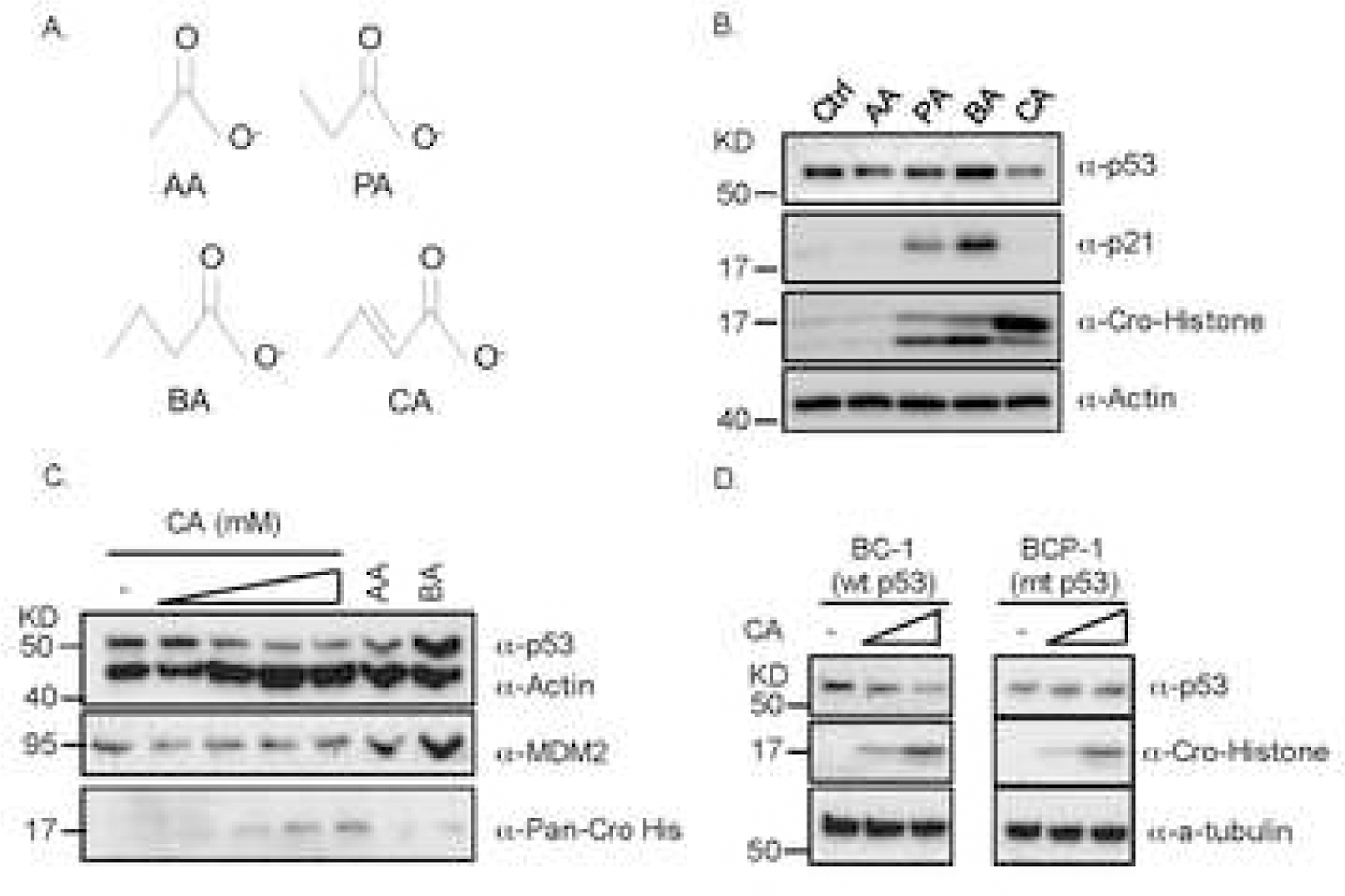
(A) The chemical structures of four short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetic acid (AA), propionic acid (PA), butyric acid (BA), and crotonic acid (CA). (B) CA reduces the protein, but not mRNA, level of p53 as well as p21 level and induces histone crotonylation. RKO cells were treated with indicated SCFAs for 24h and harvested for IB with indicated antibodies (Ctrl: Control). Portions of cells were harvested for Q-PCR analysis of p53 mRNA levels (see Fig. S1E). (C) CA reduces p53 levels in a dose dependent fashion. H460 cells were treated with different doses of CA (2,5,10 and 20mM) for 24h and harvested for IB analysis with indicated antibodies. (D) CA reduces wt, but not mutant (mt), p53 in lymphoma cells. p53-containing BC-1 and mt p53-containing BCP-1 cells were treated with two indicated doses of CA (2,5mM) for 24h and harvested for IB with indicated antibodies.
