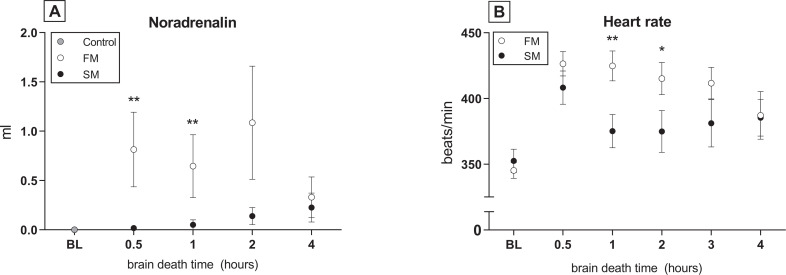
Fig 3. Inotropic support and heart rate.
Rats were subjected to fast brain death (BD) induction (intracranial pressure (ICP) increase over 1 min) versus slow BD induction (ICP increase over 30 min) and subsequently stabilized for 0.5–4 hours on a mean arterial pressure of > 80 mmHg. (A) Required noradrenalin administration for hemodynamic stabilization. (B) Heart rate of brain-dead rats during the BD stabilization period. Values are presented as mean ± SEM. Asterisks denote significant differences between the two BD models per time point: * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. X-axis 0.5–4hours–brain-dead group with period of ventilation and hemodynamic stabilization time; BL–baseline measurement before BD induction; Control–immediately sacrificed without intervention; FM–fast BD induction model, expansion of the Fogarty catheter over 1 min; SM–slow BD induction model, expansion of the Fogarty catheter over 30 min.