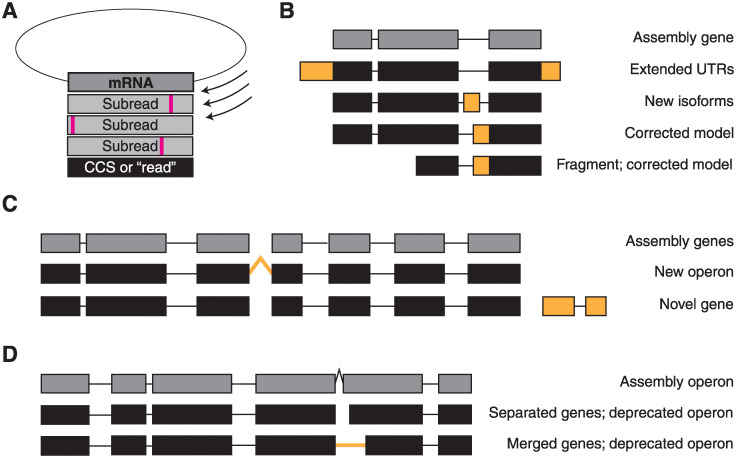
Fig 1. Improvements in gene prediction and annotation by Iso-Seq.
(A) Iso-Seq libraries are prepared by isolating and ligating mRNA into a circular backbone. The polymerase can circle the template multiple times, creating multiple “subreads” per a given template. Subreads are often error-prone, but errors are corrected by alignment and consensus calling, resulting in a circular consensus sequence (CCS, termed “read” here). (B) Reads aligning to individual genes can validate the reference model and extend UTRs, identify new isoforms by discovering novel splice sites and exons, or correct the assembly model. Notably, models can be corrected even by reads arising from fragmented mRNA with 5’ degradation. (C) Reads aligning to multiple genes can indicate a new operon, and reads mapping to intergenic sequences can identify novel genes. (D) Reads aligning to an assembly operon may direct the deprecation of the operon by separating the genes or by merging the genes into a single model.