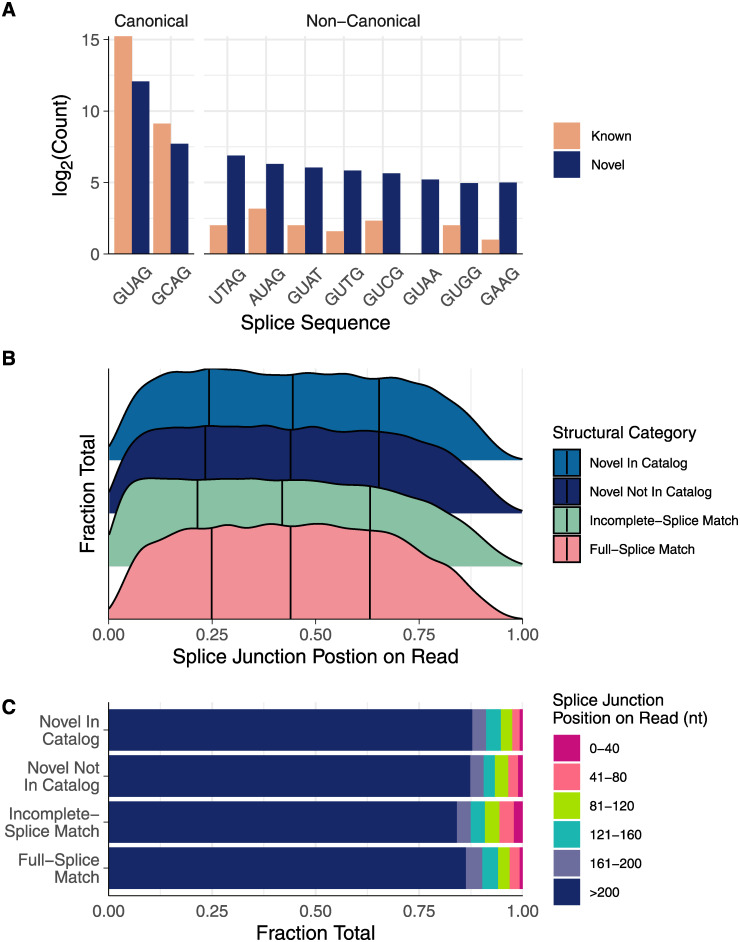
Fig 4. Iso-Seq adds to the catalog of splice junctions and identifies unannotated isoforms.
(A) The 10 most abundant splice junctions in B. malayi. Most splice junctions mapped by reads were either the canonical G[UC]-AG, but a large portion of novel splice junctions identified were non-canonical, indicating the utility of Iso-Seq for identifying non-canonical junctions. (B and C) Transcripts typically contain splice junctions equally within the middle 50% of the transcript, while junctions in the first 10% and last 25% are rarer. Incomplete-splice match (ISM) reads contain a higher proportion of splice junctions at the 5’ end of the read when compared to full-splice matches, novel in catalog (NIC) reads, and novel not in catalog (NNC) reads. This suggests that ISMs represent degraded mRNA, while NIC and NNC reads likely represent true novel isoforms or transcripts with corrected splice sites.