FIGURE 3.
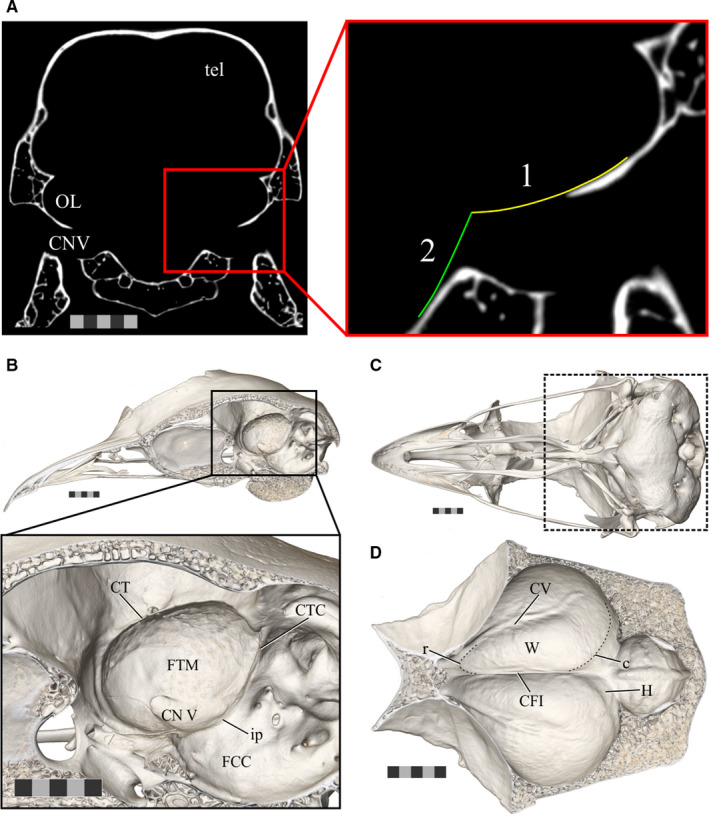
The boundaries of the endocast structures of interest. (a) An axial slice of CT scan data of Anas platyrhynchos (USNM Birds 631963) demonstrating the boundaries used to guide removal of the trigeminal ganglion from the optic lobe when generating endocasts for the present study. (1) Indicates the ventrolateral curvature of the fossa tecti mesencephali and (2) indicates the angle of the brainstem. (b) The sagittally hemisected skull of a ruffed grouse (Bonasa umbellus, AMNH Birds SKEL 21616) in a dorsolateral oblique view, with an inset zoomed in to focus on the fossa tecti mesencephali in which the optic lobe sits. (c) Ventral view of the skull of a ruffed grouse to provide orientation for (d). The area of focus of (d) is indicated by the box outlined in a dashed line. (d) A ventral view of the dorsal surface of the inside of the braincase of a ruffed grouse showing the Wulst on both hemispheres. Scale bars = 5 mm. Abbreviations: c, caudal boundary of the Wulst (subtle inflection between the Wulst and impression of hippocampus); CFI, crista frontalis interna; CTC, crista tecti caudalis; CT, crista tentorialis; CV, crista vallecularis; FCC, fossa cranii caudalis; FTM, fossa tecti mesencephali; H, impression of the hippocampus; ip, inflection point between the FCC and FTM; OL, optic lobe; r, rostral boundary of the Wulst; tel, telencephalon; TrO, impression of the tractus opticus; CN V, trigeminal nerve; W, Wulst. Scale bars = 5 mm
