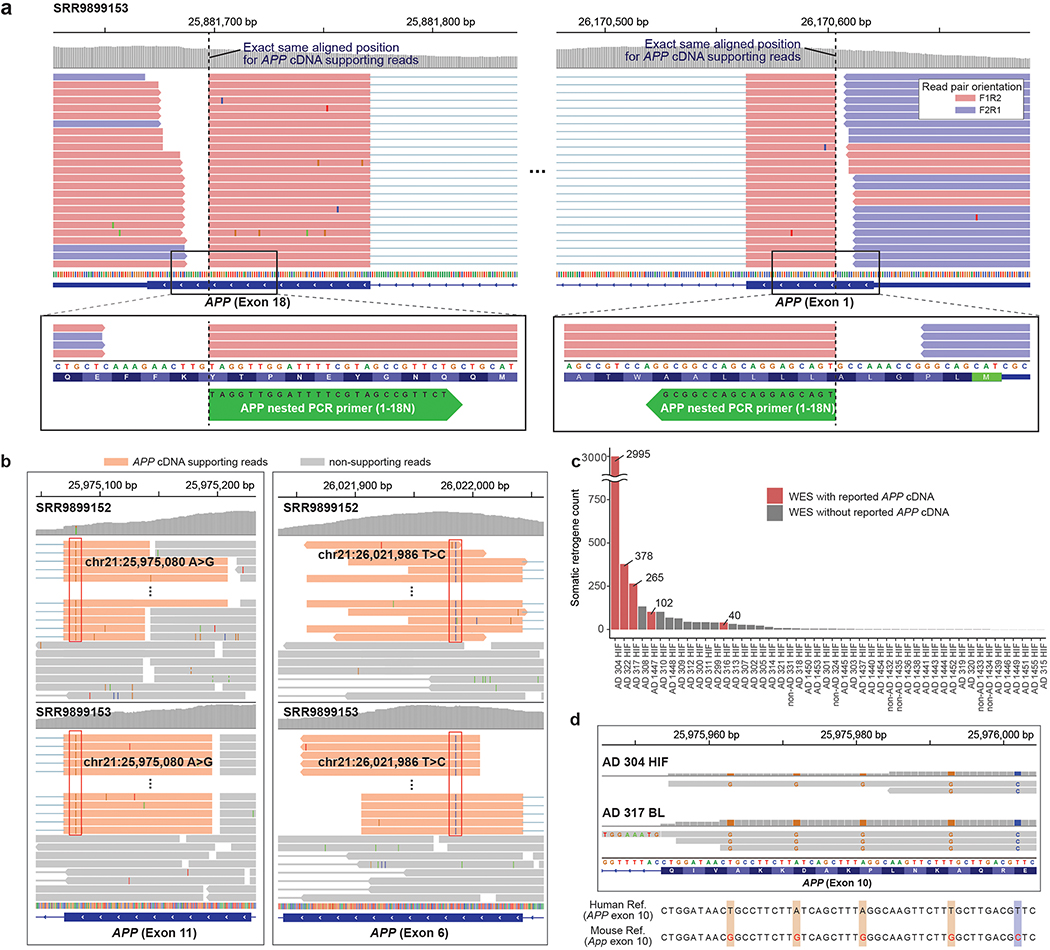
Figure 2. APP cDNA-supporting reads originate from exogenous PCR products and genome-wide human and mouse mRNA contamination.
a. APP nested PCR products found in the recent Lee WES data. Reads supporting APP cDNA are aligned to the target sites (dotted lines) of the nested PCR primers (green arrows at the bottom) used in the original Lee study. All these cDNA-supporting reads contain an IEJ between exon 2 and 17 (full structure not shown). b. The same unannotated variants found at two different positions (red boxes) only in cDNA supporting reads (orange) in both WES datasets by Lee et al. (SRR989152 and SRR989153). c. Total gene counts with potential somatic retrogene insertions in the Park et al. data. WES data with reported APP cDNA are marked in red. d. APP cDNA-supporting reads originating from mouse mRNA in the Park data. Mouse-specific single-nucleotide polymorphisms (colored bases) are observed in a portion of cDNA-supporting reads, including those with clipped sequences for exon-exon junctions, suggesting the reads originated from mouse mRNA rather than genomic DNA (see also Supplementary Fig. 1).