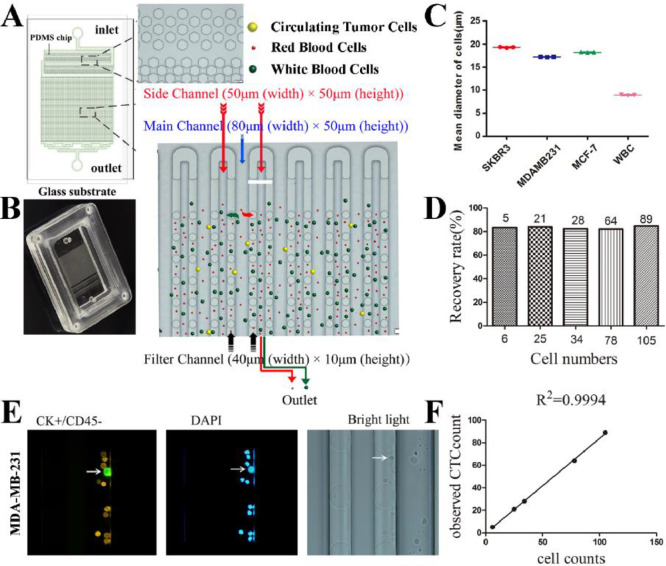
Fig. 1.
Design and operation of the size-based microfluidic device and Cell lines staining and test for capture rates. (A) Diagrammatic sketch of the microfluidic chip: the inlet, the filtration area, the Side channel, PDMS support pillars, and the outlet. The illustration shows the structure of the bulk filtration area and single cell filtration area under a microscope. The isolation strategy of the microfluidic chip (lower right). (B) Physical map of the micro-fluidic chip. (C) Three repeated gauges for the mean diameter of SKBR3, MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 and normal lymphocytes. (D) Plot of MDA-MB-231 cell recovery with the flow rate of 10 mL/h. (E) staining of MDA-MB-231 cells and leukocytes. (F) Each point represents the ratio of observed tumor cells to the expected number of cells.