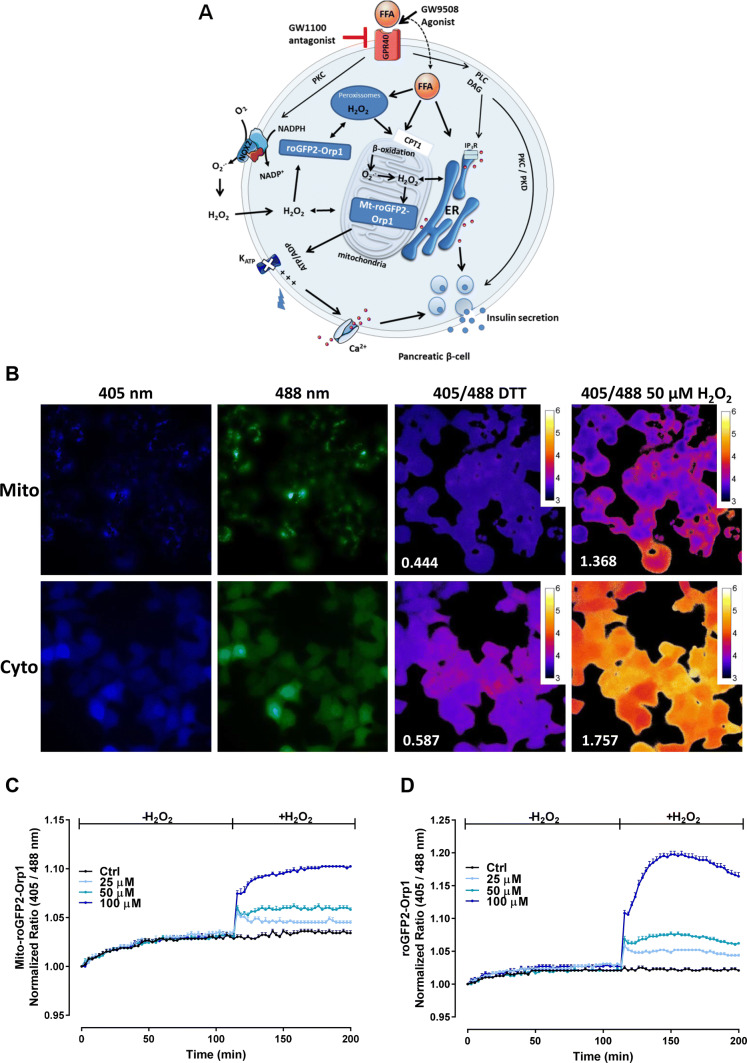
Fig. 1.
Signaling pathways activated by FFA and GPR40 agonists. a FFAs can enter the cells and be translocated to the mitochondria via carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) to be oxidized by β-oxidation. Long- and very-long-chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes, which generates H2O2. Long-chain saturated or unsaturated FFAs can also bind to Gαq-protein-coupled receptor GPR40 located in the plasma membrane. Acute activation of GPR40 by FFAs or agonists as GW9508 activates the phospholipase C (PLC) / diacylglycerol (DAG) pathway, which, respectively, activates PKC and mobilizes calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), potentiating the insulin release. GPR40 activation also activates PKD1, which acts on actin filaments to increase insulin secretion. Both activation of PKC and the β-oxidation may lead to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the cytosol by the NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) complexes and by the electron transport chain in the mitochondrial matrix, respectively. Specific sensors for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) targeted to the mitochondrial matrix (Mt-roGFP2-Orp1) or in the cytosol (roGFP2-Orp1) were used herein to assess the H2O2 production by different compartments. b Fluorescence of BRIN-BD11 cells expressing roGFP2-Orp1 in the mitochondrial matrix (Mito) or in the cytosol (Cyto) following excitation at 405 nm or 488 nm and the ratio (405/488) after addition of 10-mM DTT or 50-µM H2O2. Numbers represent the non-normalized ratio after addition of DTT or 50 µM H2O2. c, d Response of Mt-roGFP2-Orp1 (c) or roGFP2-Orp1 cells (d) expressed in BRIN-BD11 exposed to exogenously applied H2O2 at the concentrations indicated