Fig 2. GST detoxification.
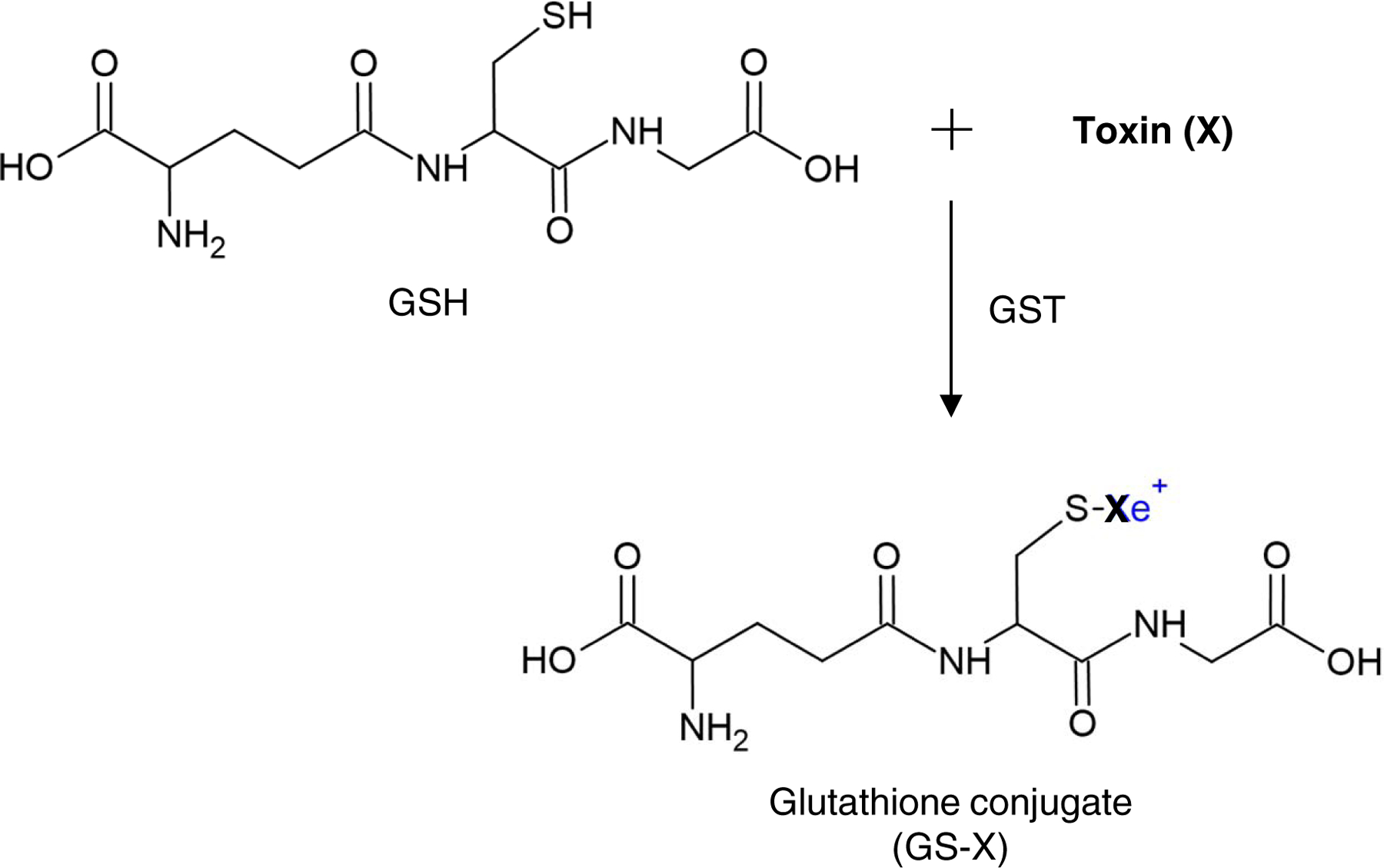
GSTs are a family of phase II detoxification enzymes that catalyze the conjugation of a wide variety of endogenous and xenobiotic toxins (X), to the -SH group of reduced glutathione (GSH), resulting in the formation of glutathione conjugate (GS-X). Glutathione conjugates are metabolized further by cleavage of the glutamate and glycine residues, followed by acetylation of the resultant free amino group of the cysteinyl residue to produce a very hydrophilic product, mercapturic acid, which is then eliminated from the cell through the transmembrane transporters.
