Fig 3. Detoxification of 4-HNE by GSTA isoforms.
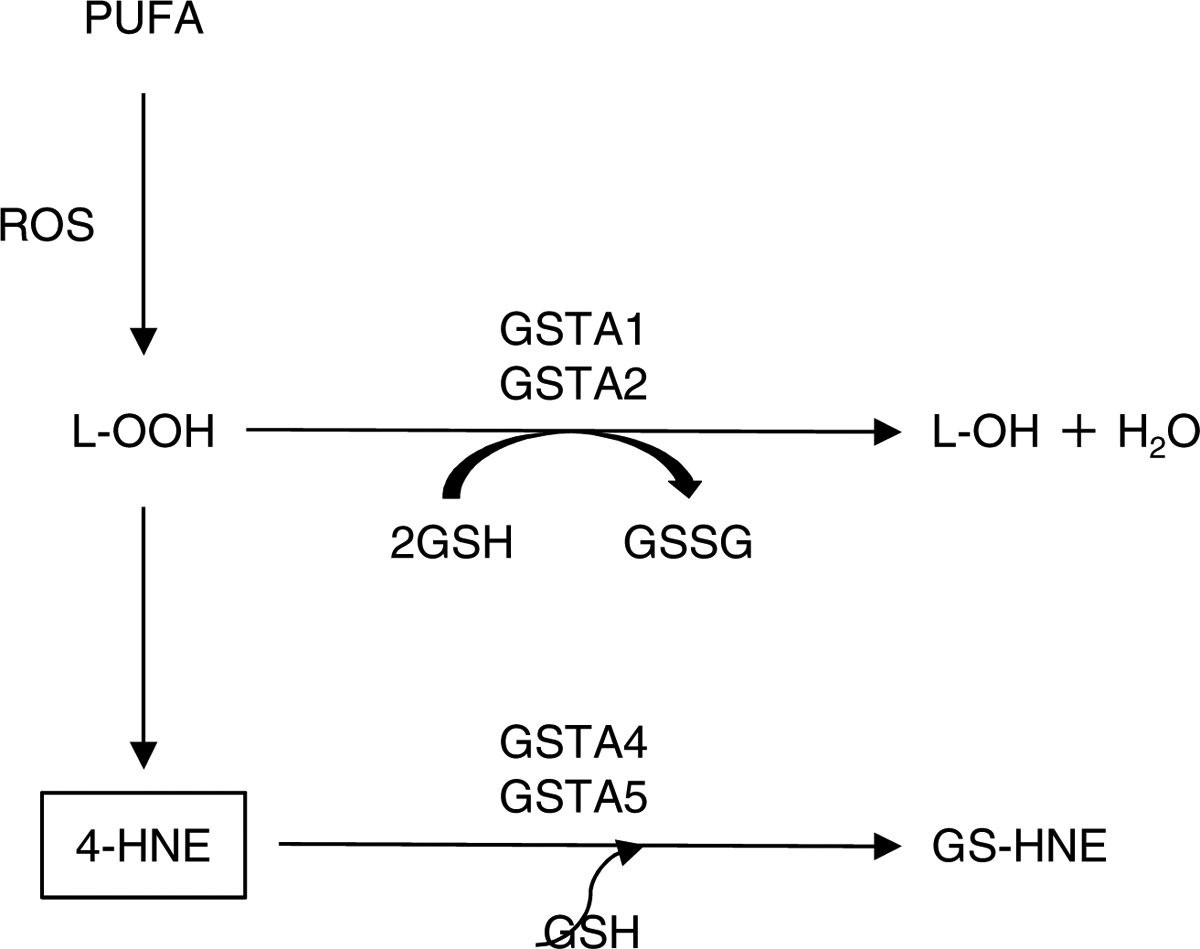
GSTA1, GSTA2, GSTA4, and GSTA5 are thought to be the major determinants of the intracellular concentration of 4-HNE. GSTA1 and GSTA2 can catalyze GSH-dependent reduction of lipid hydroperoxide (L-OOH). L-OOH is then reduced to the corresponding alcohol (L-OH) with oxidized glutathione (GSSG) and water as by-products, thereby blocking the formation of 4-HNE. GSTA4 and GSTA5 conjugate 4-HNE to GSH, forming a GSH-4-HNE conjugate (GS-HNE), which is then eliminated from the cell through the transmembrane transporters. PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acid (i.e., linoleic acid, linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid).
