Fig 4. Role of NRF2 in GSTA detoxification of 4-HNE in cochlea.
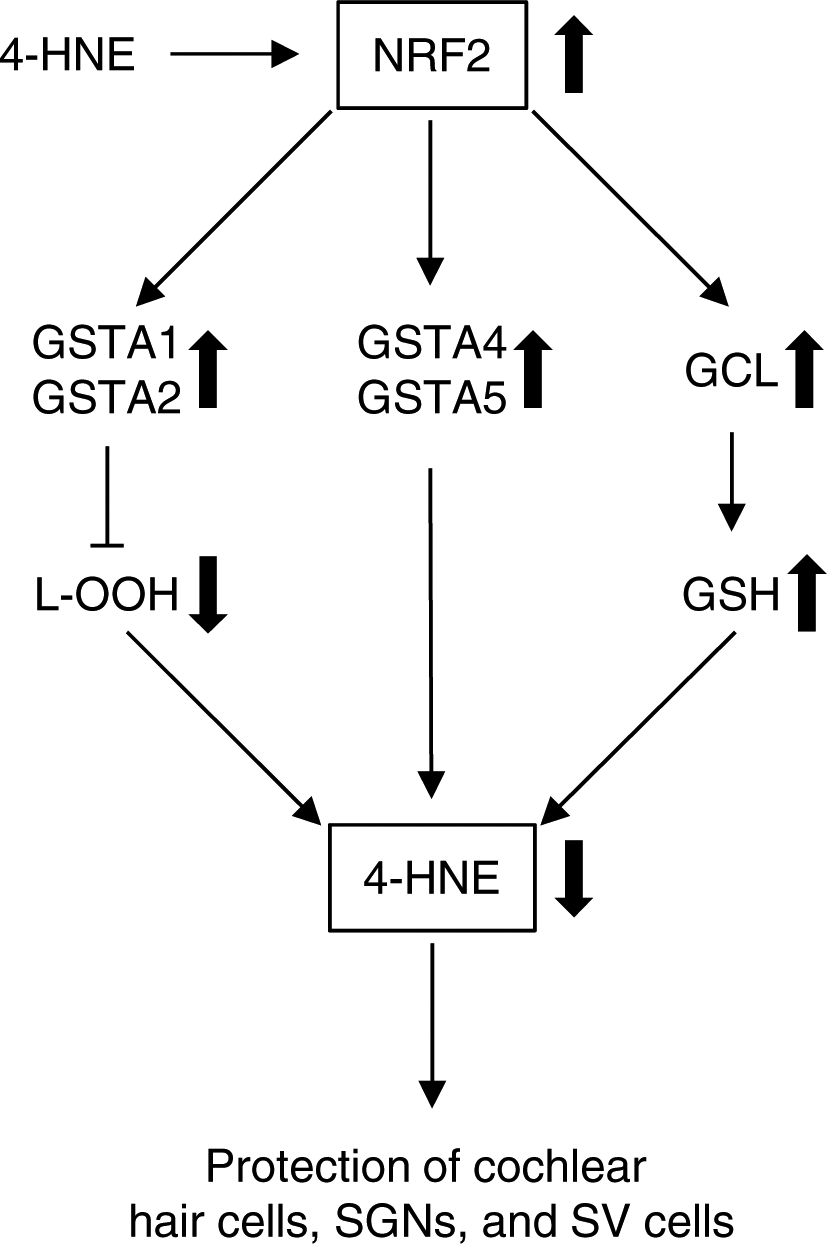
NRF2 promotes the transcriptional induction of antioxidant genes such as the subunits of glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL), the rate-limiting enzyme in glutathione biosynthesis, and phase II detoxification genes, including GSTA genes, including GSTA1, GSTA2, GSTA4, and GSTA5. 4-HNE can also act as a direct activator of NRF2. When exposed to noise or ototoxic drug or in aged cochlear tissues, higher oxidative stress likely leads to accumulation of 4-HNE. This can trigger the activation of NRF2, which in turn activates GSTA1 and GSTA2, blocking the formation of 4-HNE, and or activates GSTA4 and GSTA5, conjugating 4-HNE to GSH. This results in elimination of 4-HNE and protecting cochlear hair cells, SGNs, and SV cells. In addition, GSH can directly sequester 4-HNE through its cysteine residues by the formation of GS-HNE adducts.
