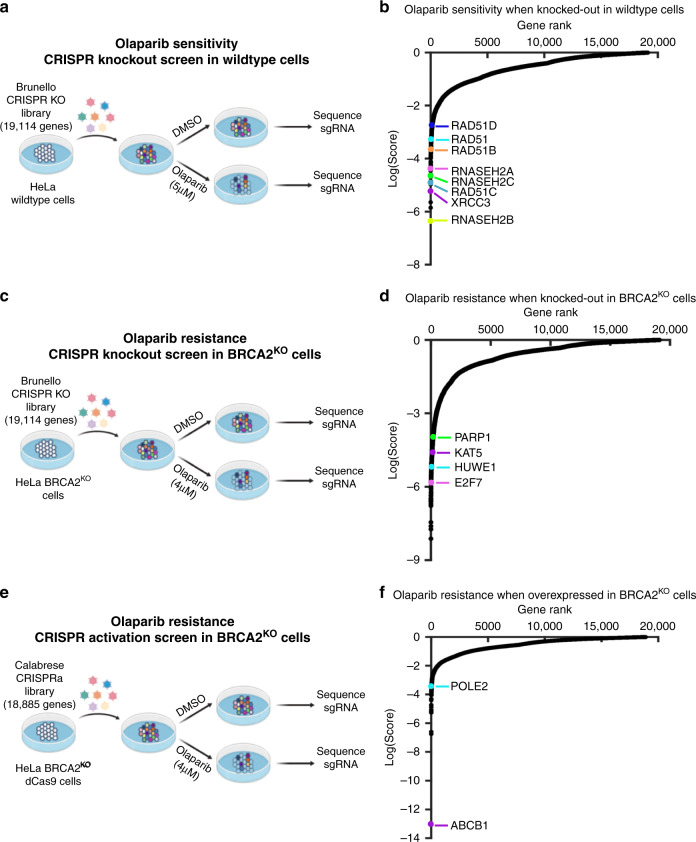
Fig. 1. Complementary CRISPR knockout and activation screens identify determinants of PARPi response in parental or BRCA2-knockout HeLa cells.
a Schematic representation of the CRISPR knockout screen for olaparib sensitivity in wildtype cells. HeLa cells were infected with the Brunello CRISPR knockout library. Infected cells were divided into PARP inhibitor (olaparib)-treated or control (DMSO) arms. Genomic DNA was extracted from cells surviving the drug treatment and single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) were identified using Illumina sequencing. b Scatterplot showing the results of this screen. Each gene targeted by the library was ranked based on the MAGeCK negative selection score. Several biologically interesting hits are highlighted. c Schematic representation of the CRISPR knockout screen for olaparib resistance in BRCA2KO cells. HeLa BRCA2KO cells were infected with the Brunello CRISPR knockout library. Infected cells were divided into PARP inhibitor (olaparib)-treated or control (DMSO) arms. d Scatterplot showing the results of this screen, with several biologically interesting hits highlighted. Each gene targeted by the library was ranked based on the MAGeCK positive selection score. e Schematic representation of the CRISPR activation screen for olaparib resistance in BRCA2KO cells. HeLa BRCA2KO cells stably expressing the modified dCas9 enzyme were infected with the Calabrese CRISPR activation library. Infected cells were divided into PARP inhibitor (olaparib)-treated or control (DMSO) arms. f Scatterplot showing the results of this screen, with several biologically interesting hits highlighted. Each gene targeted by the library was ranked based on the MAGeCK positive selection score. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.