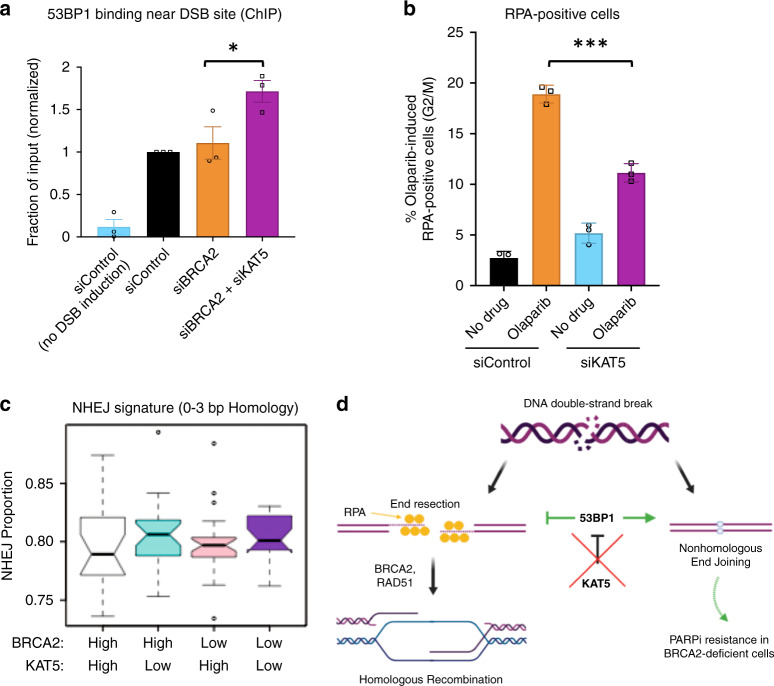
Fig. 6. Functional consequences of KAT5 depletion.
a Depletion of KAT5 leads to increased recruitment of 53BP1 near the site of the double-strand break in BRCA2-depleted U2OS-DSB reporter cells. DSBs were generated at a specific genomic locus through induction of expression of LacI-FokI nuclease. Then, chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with an antibody against 53BP1 and qPCR was performed using primers for the DSB site. The averages of three experiments are shown, with standard error of the mean as error bars. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (t-test, two-tailed, paired). b KAT5 loss leads to a reduction in olaparib-induced end resection as measured by quantification of RPA-positive cells. Cells were treated with 10 μM olaparib for 12 h before being harvested for flow cytometry experiments using an RPA antibody. Representative gating of these experiments is shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. The averages of three experiments are shown, with standard deviations as error bars. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (t-test, two-tailed, unequal variance). c Bioinformatic analysis of the OV-AU dataset reveals that KAT5 low tumors show increased NHEJ signature at structural variations breakpoints, as compared to KAT5 high tumors, in both BRCA2 high and BRCA2 low backgrounds. The 93 samples in the cohort were distributed into four categories based on combinatorial high (above median) and low (below median) expression of BRCA2 and KAT5. In the box plots, lower and upper hinges correspond to the first and third quartiles; upper and lower whiskers extend to 1.5 × interquartile range; the line in the box indicates the median; outlier data are shown as points. d Proposed model for resistance caused by KAT5 depletion. In BRCA2-proficient cells, homologous recombination is the most accurate mechanism of double-strand break repair. However, this pathway is not functional in BRCA2-deficient cells. KAT5 depletion increases 53BP1 binding at the double-strand break in BRCA2-deficient cells, preventing the break from proceeding down the dead-end process of HR and instead directs it towards repair by NHEJ. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.