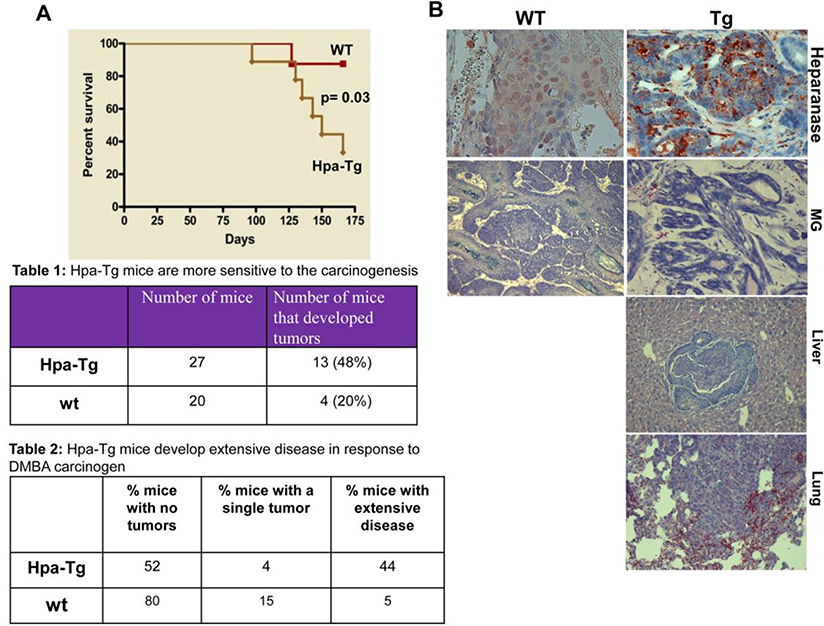
Figure 1. Hpa-tg mice are more susceptible to DMBA carcinogenesis.
A. Control (Con) and Hpa-tg mice were administrated 4 times with DMBA (p.o; 1.5 mg/mouse) and mouse survival rates were recorded. B,C. DMBA (p.o; 1 mg/mouse) was similarly administrated, and mice were sacrificed once tumors became apparent or mice became morbid. At termination, tumor development was inspected in all internal organs and categorized as no, single, or extensive disease (C) according to visual inspection and histology (B). Mammary gland (MG) tumors in WT and Hpa-tg mice and tumors developed in the liver and lungs of Hpa-tg mice were subjected to immunostaining applying anti-heparanase antibody (B). Table 1 denotes the percentage of tumor-bearing Hpa-tg vs. WT mice. Table 2 denotes the percentage of Hpa-tg vs. WT mice with no tumors, single tumor or extensive disease.