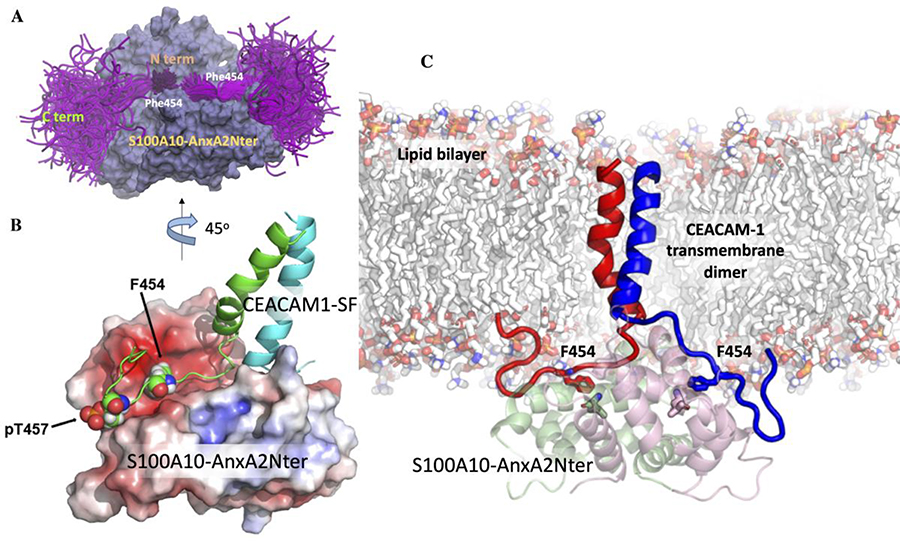
Figure 6. The ensemble of cytoplasmic domain of CEACAM1-SF conformations and its predicted binding mode to S100A10-AnxA2Nter pseudo dimer.
A: S100A10-AnxA2Nter (light blue) and cytoplasmic domain peptide of CEACAM1-SF (magenta). Positions of N- and C-termini and Phe454 are indicated. B: Molecular model of two (green and cyan) TM-cytoplasmic domains of CEACAM1-SF interactions with S100A10-AnxA2Nter pseudo dimer (lipid bilayer removed for clarity). Electrostatic surfaces (red for negative blue for positive). Phe454 and Thr457 are shown as space filling spheres to indicate their binding poses to one of the S100A10 dimers. Each Phe454 packs against L78 of S100A10. Thr457 is modeled as pT457 to indicate its proposed electrostatic repulsion. C: Predicted structure of the CEACAM1-SF dimer bound to S100A10-AnxA2Nter pseudo dimer in an embedded lipid bilayer. The contacting residues Phe454 of CEACAM1-SF are shown as sticks (EC domains of CEACAM1-SF not shown).