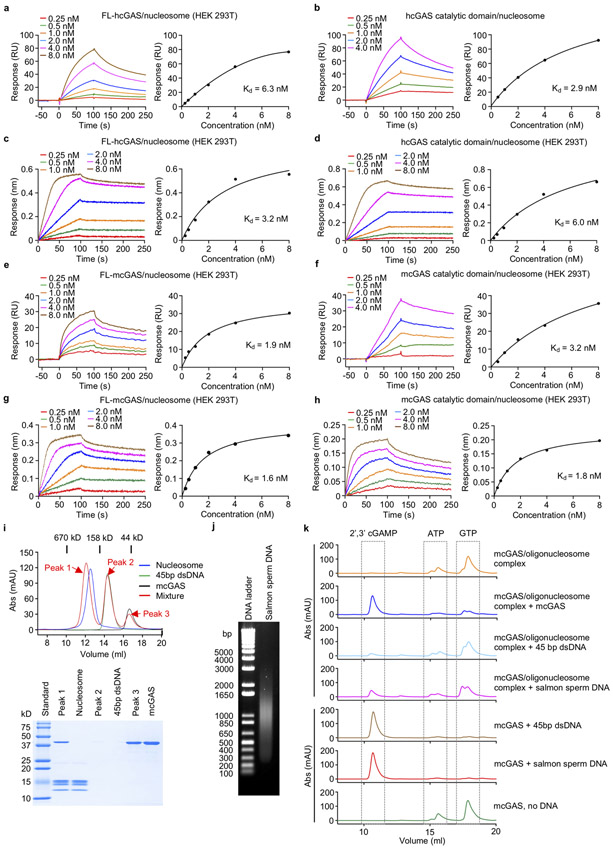
Extended Data Figure 2. cGAS-nucleosome binding studies and activity assays of cGAS-nucleosome complex.
a. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) showing that full length human cGAS binds to nucleosomes purified from HEK 293T cells with nanomolar affinity.
b. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) showing that human cGAS catalytic domain binds to reconstituted nucleosomes with nanomolar affinity.
c-d. Bio-Layer interferometry binding studies of full length human cGAS and its catalytic domain with nucleosomes (HEK 293T).
e-f. SPR binding studies show that full length mouse cGAS and its catalytic domain bind nucleosomes (HEK 293T) with nanomolar affinities.
g-h. Bio-Layer interferometry binding studies of full length mouse cGAS and its catalytic domain with nucleosomes (HEK 293T).
i. Gel filtration chromatography (top panel) and SDS-PAGE (lower panel) analyses of 45 bp ISD dsDNA, nucleosome and cGAS mixture show that the nucleosome efficiently competes with dsDNA to bind cGAS.
j. Agarose gel electrophoresis of the salmon sperm DNA used in cGAS activity assays.
k. cGAS activity assays by ion exchange chromatography show that oligonucleosome binding potently inhibits the activity of cGAS and ligand free cGAS can be activated by the cGAS-oligonucleosome complex.