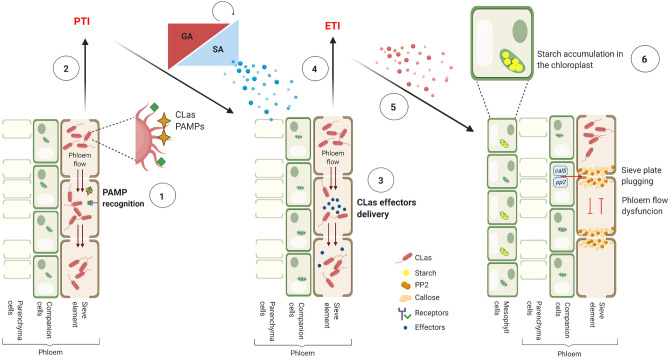
Figure 4.
Defense response of susceptible genotypes against CLas. In the phase 1 of this model, citrus plants receptors detect the CLas PAMPs. In phase 2, a PAMP-triggered immunity (PTI) response is initiated, resulting in the production of gibberellic acid (GA), salicylic acid (SA) and the SA-dependent gene expression activation (in blue). In phase 3, CLas deliver effectors leading in effector-triggered susceptibility (ETS). In phase 4, effectors are recognized by plants proteins, activating effector-triggered immunity (ETI). In phase 5, ETI triggers a series of genetic events (in red), including the induction of calloses synthases and pp2 expression. This exaggerated response could be considered as hypersensitive cell death (HR), since the attempt to isolate spatially the CLas leading to callose and PP2 accumulation, that cause phloem dysfunctions. The phase 6 represents the starch accumulation in the mesophyll chloroplasts(Created with BioRender.com).