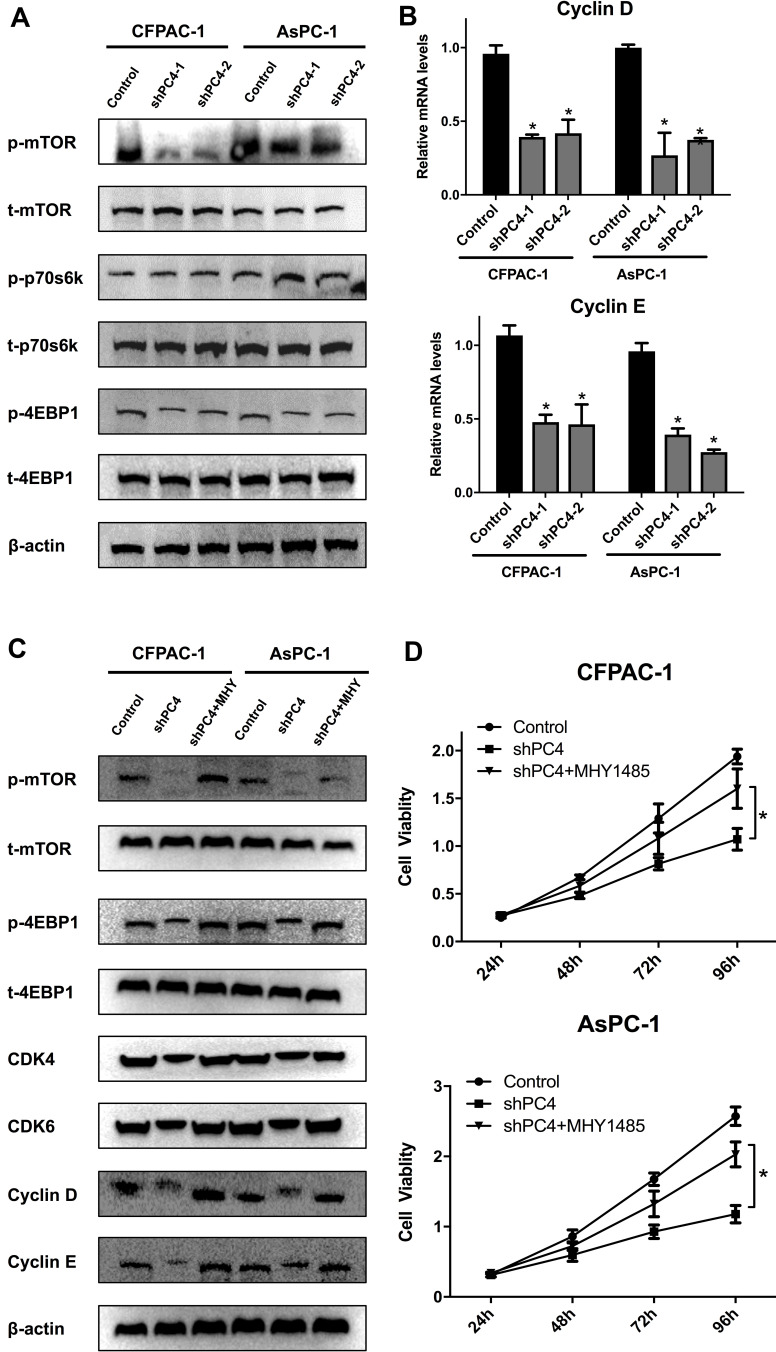
Figure 4.
PC4 knockdown suppressed the activation of the mTOR/p70s6k signaling pathway in AsPC-1 and CFPAC-1 cells. (A). Western blot analysis of p-mTOR, t-mTOR, p-p70s6k, t-p70s6k, p-4EBP1 and t-4EBP1 protein levels in AsPC-1 and CFPAC-1 cells with stable PC4 knockdown and corresponding controls. (B). qPCR of Cyclin D and Cyclin E mRNA levels in each group. (C). Western blot analysis of p-mTOR, t-mTOR, p-p70s6k, t-p70s6k, CDK4, CDK6, Cyclin D and Cyclin E protein levels in AsPC-1 and CFPAC-1 cells with stable PC4 knockdown in the presence or absence of 2 nmol/L MHY1485 for 1 h and the corresponding controls. (D). Cell viability in each group was evaluated by a CCK-8 assay. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05, compared to the control.
Abbreviations: SD, standard deviation; p-mTOR, phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin; t-mTOR, total mammalian target of rapamycin, CCK-8, cell counting kit-8.