Figure 3.
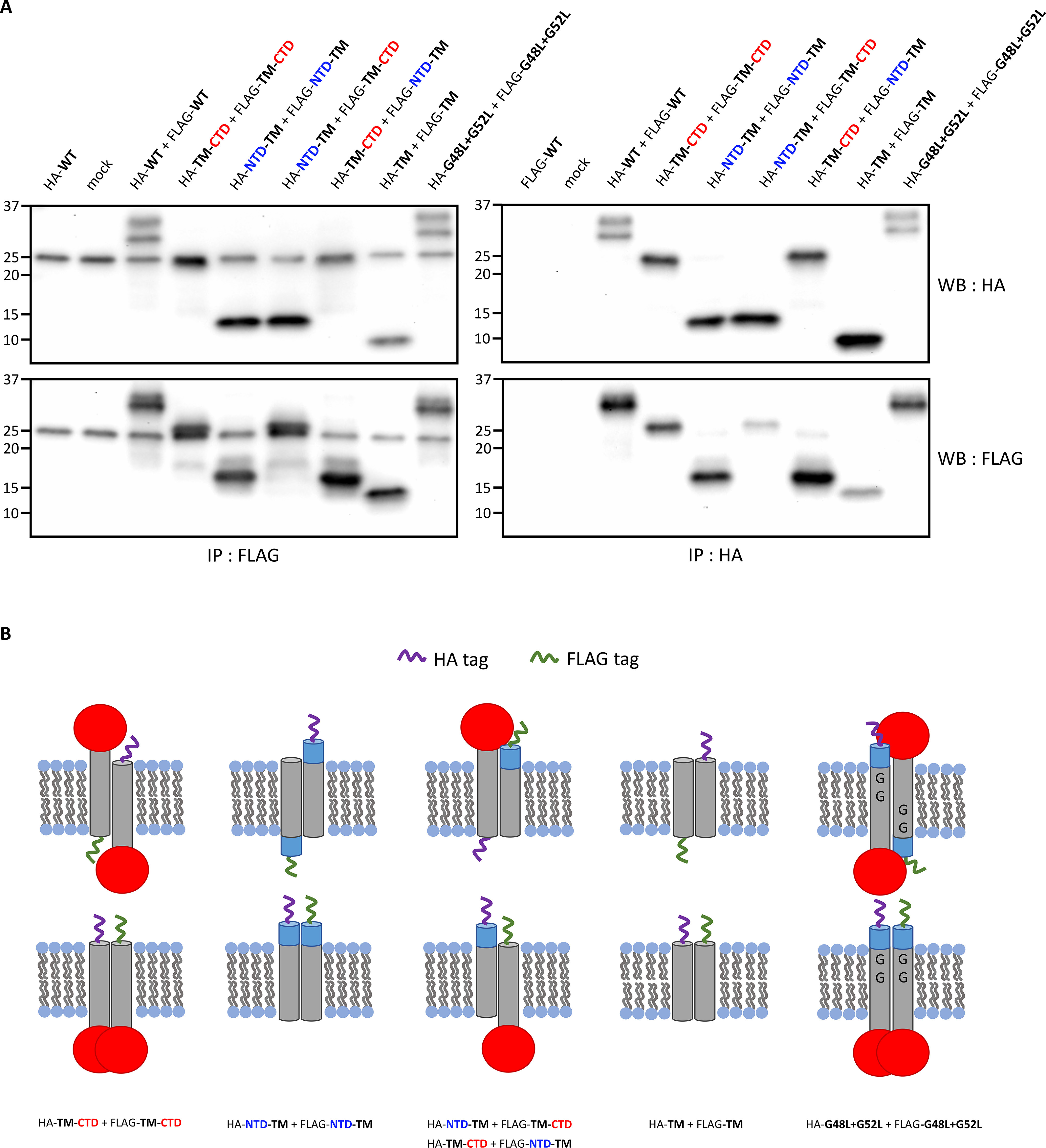
MRAP2 dimerizes through its transmembrane domain. A, HEK293T cells are co-transfected with HA- and FLAG-tagged versions of the following MRAP2 constructs: N-terminal domain truncation (TM-CTD), C-terminal domain truncation (NTD-TM), the transmembrane domain alone (TM), or a mutant that replaces the glycine residues within the transmembrane domain with leucine residues (G48L+G52L). Co-immunoprecipitations from cell lysates followed by immunoblotting show that neither the N-terminal domain, the C-terminal domain, nor the glycine residues in the transmembrane domain are required for dimerization of MRAP2. B, schematic depicting the co-immunoprecipitated HA- and FLAG-tagged MRAP2 dimers. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blotting.
