Table 1.
An overview on IFN-inducing effects of the antiviral agents. The clinical trial data was gathered on 17 September 2020. Molecular structures of the following drugs are shown as a representative of their classes; for instance, neomycin for aminoglycosides, idarubicin for anthracyclines, and simvastatin for statins. All structures are adapted from PubChem [37].
| Drug/Drug class | Molecular structure | Therapeutic category | Antiviral activity | COVID-19-related studies | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Azithromycin | 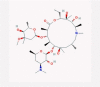 |
Antibiotic | Binding to IFNAR1 complex and ISGF3 upregulation/potentiating IFN type I signaling | 112 clinical trials specifically on azithromycin/Amplifying the effect of hydroxychloroquine | [38], [39], [40], [41], [42] |
| 2 | Aminoglycosides | 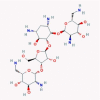 |
Antibiotic | ISG induction, suppress replication via binding to promotor RNA | No data found | [38], [43], [44] |
| 3 | Nitazoxanide | 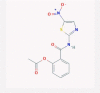 |
Amebicide | IFN signaling, autophagy promotion | 20 clinical trials in combination with azithromycin or hydroxychloroquine/Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture | [38], [45], [46], [47], [48], [49], [50] |
| 4 | Niclosamide | 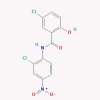 |
Anthelmintic | Inhibition of SARS-CoV 3CL protease, prevention of viral entry | Six clinical trials are enrolling./Suggested as an inhibitor of autophagy and viral replication | [45], [51], [52], [53] |
| 5 | Itraconazole | 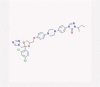 |
Antifungal | Lanosterol 14α-demethylase inhibition, IFN A/B increase | No data found. | [38], [54] |
| 6 | Ribavirin | 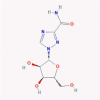 |
Antiviral | Inhibition of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase/RdRp antagonism/causing error catastrophe | Suggested as a COVID-19 therapy/Suggested RdRp antagonist in an in silico study/Twelve clinical trials are enrolling | [45], [52], [55], [56] |
| 7 | Anthracyclines | 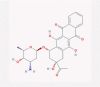 |
Antibiotic | Enhancement in ISRE activity, inhibition of RNA and DNA synthesis | Idarubicin was suggested as a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 endoribonuclease by an in silico study | [38], [57], [58], [59], [60] |
| 8 | Tamoxifen | 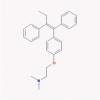 |
Anti-neoplastic | Multistep inflammation inhibitor | One clinical trial in combination with isotretinoin | [45], [52], [61] |
| 9 | Gefitinib | 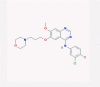 |
EGFR inhibitor | Inhibition of the NF-kB pathway and viral replication | No data found | [38], [62] |
| 10 | Trametinib | 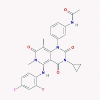 |
Multi-kinase inhibitor | Induction of IRF1 and IFN-κ | No data found | [45], [63] |
| 11 | Gemcitabine | 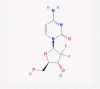 |
Anticancer | DNA synthesis inhibition | Predicted to have positive effects through AI analysis | [38], [64], [65] |
| 12 | Obatoclax | 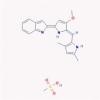 |
Anticancer | Suppression of viral endocytic uptake | No data found | [38], [66] |
| 13 | Sirolimus | 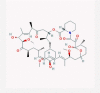 |
Immunosuppressant | Entry inhibitor, downregulation of CCR5 | Suggested in an interactome-based bioinformatics study/Six clinical trials are enrolling | [38], [52], [67], [68] |
| 14 | Mycophenolic acid | 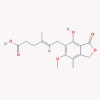 |
Immunosuppressant | ISGs upregulation | Recognized as the most potent compound against the envelope protein and nucleocapsid phosphoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 by a docking study | [45], [69], [70] |
| 15 | Aspirin | 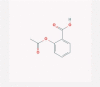 |
NSAID | COX-2 inhibition, p38 MAPK and MEK1/2 activation | Fourteen clinical trials are enrolling | [38], [52], [71] |
| 16 | Indomethacin | 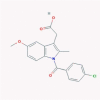 |
NSAID | Production of 2′,5′-OAS, Th1 response enhancement, viral RNA synthesis block | Two clinical trials are enrolling. Opined for use in positive SARS-CoV-2 patients who have no cytokine storm |
[38], [52], [72], [73] |
| 17 | Metformin | 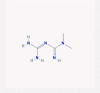 |
Anti-hyperglycemic | Promoting cells’ insulin sensitivity/JAK/STAT pathway activation | In silico suggestion as an interferer with Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase α gene | [38], [74], [75], [76] |
| 18 | Fluoxetine | 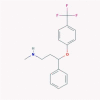 |
Antidepressant | JAK/STAT1 activation | Two clinical trials are enrolling | [38], [52], [77] |
| 19 | Verapamil | 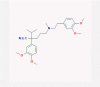 |
Calcium channel blocker | Cell entry inhibition | Three clinical trials are enrolling | [38], [52], [78] |
| 20 | Statins | 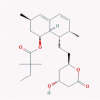 |
Anti-hypercholesterolemia | Prenylation inhibition, reduction of cell-to-cell fusion | Eleven clinical trials are enrolling./Hypothesized to be effective because of immunomodulatory effect and cardiovascular damage.Recommended for use in patients with cardiovascular disease history | [45], [52], [79], [80], [81] |
| 21 | Caffeine | 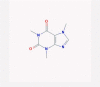 |
CNS stimulant | COX-2, HSP90, and Ras-ERK inhibition | Four clinical trials are enrolling | [45], [52], [82] |
| 22 | Glycyrrhizin | 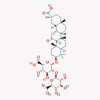 |
Anti-inflammatory | Downregulation of ROS formation, NF-κB, JNK, and p38 MAPK | Suggested as a potential drug because of ACE2 binding, proinflammatory cytokine downregulation, and ROS accumulation inhibition | [45], [83], [84] |
| 23 | Berberine | 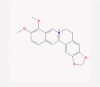 |
Antiseptic | Stimulation of Th1 response and IFN-γ | One clinical trial is enrolling | [45], [85], [86] |
2′, 5′-OAS: 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthase/ACE: angiotensin converting enzyme/CoA: co-enzyme A/COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019/COX: cyclooxygenase/ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase/HSP90: heat shock protein 90/IFN: interferon/IFNAR: type I interferon receptor/IRF: interferon-regulatory factor/ISG: interferon-stimulated gene/ISGF: interferon-stimulated gene factor/ISRE: interferon-stimulated response element/JAK: Janus kinase/MEK: mitogen-activated protein kinase/NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB/RdRp: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase/ROS: reactive oxygen species/SARS-CoV: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease/STAT: transducer and activator of transcription/Th: T helper cell.
