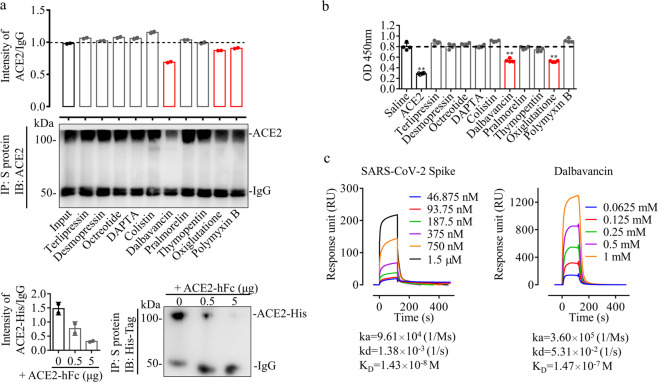
Fig. 2. Dalbavancin inhibits binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to ACE2 in vitro.
a ACE2 (0.5 μg) and SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (0.5 μg) were mixed and treated with various candidate peptide drugs (10 μM). Co-precipitated proteins were identified by western blot analysis using anti-ACE2 antibody. Analyzed proteins are indicated on the right. For positive control (bottom), ACE2-His (0.5 μg) and SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (0.5 μg) were mixed and treated with various concentration of ACE2-hFc, and then co-precipitated proteins were identified by western blot analysis using anti-His-tag antibody. b ACE2 (2 μg/ml) was crosslinked to microplates by N-oxysuccinimide esters for ELISA. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (10 ng/mL) and tested candidate drugs (1 μM) were incubated with ACE2, and extra un-crosslinked ACE2 protein (100 ng/mL) was used as a positive control. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibodies were used for chromogenic reaction. c Binding curves of immobilized human ACE2 with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (left, positive control) and dalbavancin (right). Concentration-response SPR experiment showing binding of dalbavancin to ACE2 with an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of ~147 nM.