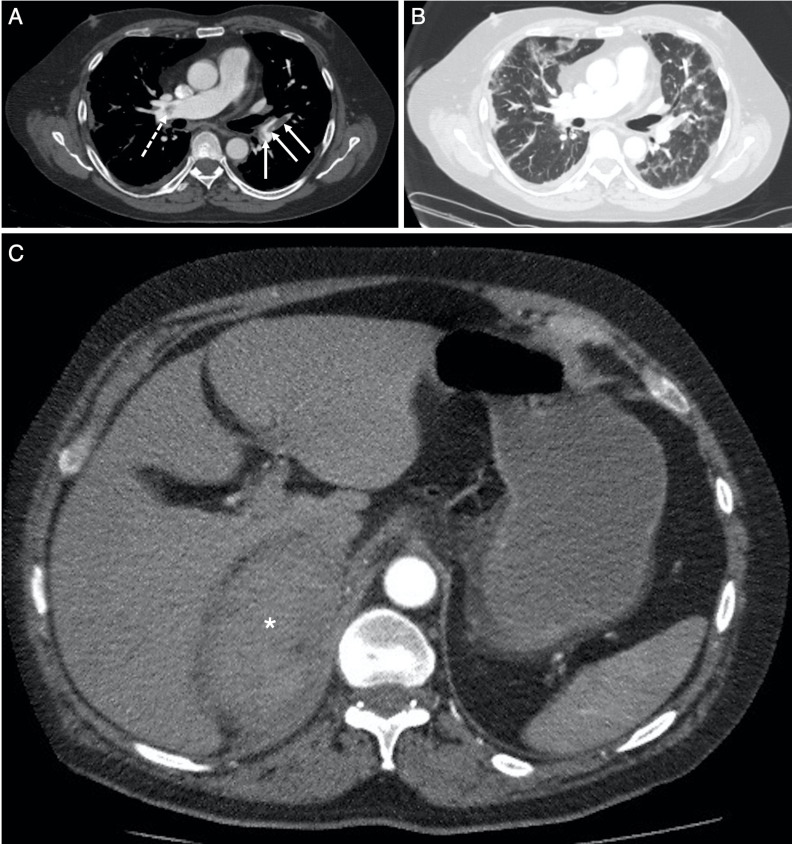
Figure 2.
Selected axial slices from the CT pulmonary angiogram obtained 5 days following the chest radiograph in figure 1B, performed for persistent oxygen requirement and a raised D-dimer result. (A) Through the level of the pulmonary trunk and right main pulmonary artery on soft-tissue window (W:450, L:50), demonstrates acute pulmonary emboli in right main pulmonary artery proximal to the trifurcation (dashed arrow) with further emboli at the origin, and within, the left lower lobe segmental pulmonary arteries (solid arrows). There was no saddle embolus, right heart strain or pericardial effusion. (B) Through the same level as (A) on lung window (W:1500, L:−50), demonstrates bilateral multifocal ground glass opacification consistent with COVID-19 infection. (C) More inferiorly in the upper abdomen, there is a soft-tissue density mass (average Hounsfield Unit, 55) in the right suprarenal region (*): the right adrenal gland is not identified, and appearances are suspicious for right adrenal haemorrhage.