Table 3.
Long-Term Abstinencea, b (≥12 Months) From e-Cigarettes, Nicotine Replacement Therapy, and Other Tobacco Productsc Among US Smokers Who Were ≥12 Months’ Cigarette Abstinent at Follow-up in 2016–2017, Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health Study
Products Abstained from for 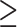 12-Months at W4 12-Months at W4
|
e-Cigarettes Used To Quit d (n = 49) | e-Cigarettes Not Used To Quit d (n = 227) | Pharmaceutical Aid e Used To Quit d (n = 45) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weighted % Abstinent | 95% CI | Weighted % Abstinent | 95% CI | Weighted % Abstinent | 95% CI | |
| e-Cigarettes | 31.7 | 16.4, 47.0 | 93.0 | 89.0, 96.9 | 96.1 | 89.7, 102.4 |
| NRT | 94.5 | 85.3, 103.8 | 91.9 | 87.4, 96.3 | 71.0 | 55.7, 86.4 |
| Other tobacco products | 82.2 | 70.0, 94.5 | 82.9 | 77.3, 88.5 | 93.1 | 85.2, 101.1 |
| Combustiblef | 83.0 | 70.7, 95.2 | 86.1 | 80.5, 91.6 | 93.1 | 85.2, 101.1 |
| Smokelessg | 93.3 | 84.0, 102.6 | 95.6 | 92.6, 98.6 | 97.2 | 91.5, 102.9 |
Abbreviations: W4, wave 4 of the study; NRT, nicotine replacement therapy.
a Abstinence of ≥12 months, reported at wave 4.
b Weighted US population estimates.
c Other tobacco products include cigars (traditional, cigarillo, and filtered), pipes, hookah, snus, or other smokeless products.
d e-Cigarette use and pharmaceutical-aid status for most recent quit attempt, among all smokers reporting a quit attempt at wave 3.
e Pharmaceutical aids include varenicline and buproprion.
f Combustible products include cigars, pipes, and hookahs.
g Smokeless products include snus, moist snuff, dip, and spit and chewing tobacco.
