Table 3.
Logistic Regression Models of the Association of the Prevalence of Smoking Versus Not 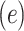 and the Smoking Intensity (
and the Smoking Intensity (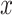 or
or  ) With the Prevalence of Confirmed Clinical Neuropathy at 13 Years of Follow-up in the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Cohort, North America, Circa 2006
) With the Prevalence of Confirmed Clinical Neuropathy at 13 Years of Follow-up in the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Cohort, North America, Circa 2006
| Model |
Coefficient (Factor) |
Estimate a | SE | P Value | Model χ 2 | df | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Noncenteredb 1: 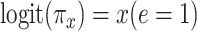
|
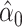
|
−0.5891 | 0.3064 | 0.0545 | 0.24 | 1 | 0.6217 |
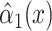
|
0.0084 | 0.0170 | 0.6217 | ||||
Noncenteredb 2: 
|
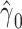
|
−0.9010 | 0.0687 | <0.0001 | 6.09 | 1 | 0.0136 |
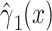
|
0.0232 | 0.0094 | 0.0136 | ||||
Noncenteredb 3: 
|
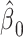
|
−0.9170 | 0.0706 | <0.0001 | 7.19 | 2 | 0.0274 |

|
0.0084 | 0.0170 | 0.6215 | ||||
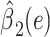
|
0.3280 | 0.3144 | 0.2969 | ||||
Centeredc 4: 
|
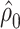
|
−0.4610 | 0.1585 | 0.0036 | 0.24 | 1 | 0.6217 |

|
0.0084 | 0.0170 | 0.6217 | ||||
Centeredc 5: 
|
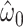
|
−0.8459 | 0.0643 | <0.0001 | 0.27 | 1 | 0.6001 |
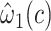
|
0.0094 | 0.0180 | 0.6001 | ||||
Centeredc 6: 
|

|
−0.9170 | 0.0706 | <0.0001 | 7.19 | 2 | 0.0274 |

|
0.0084 | 0.0170 | 0.6215 | ||||

|
0.4561 | 0.1735 | 0.0086 |
Abbreviations: df, degrees of freedom; SE, standard error.
a Estimate is the log odds ratio.
b Models with noncentered smoking intensities (x, models 1–3).
c Models with centered intensities (c, after subtracting the mean, models 4–6).
