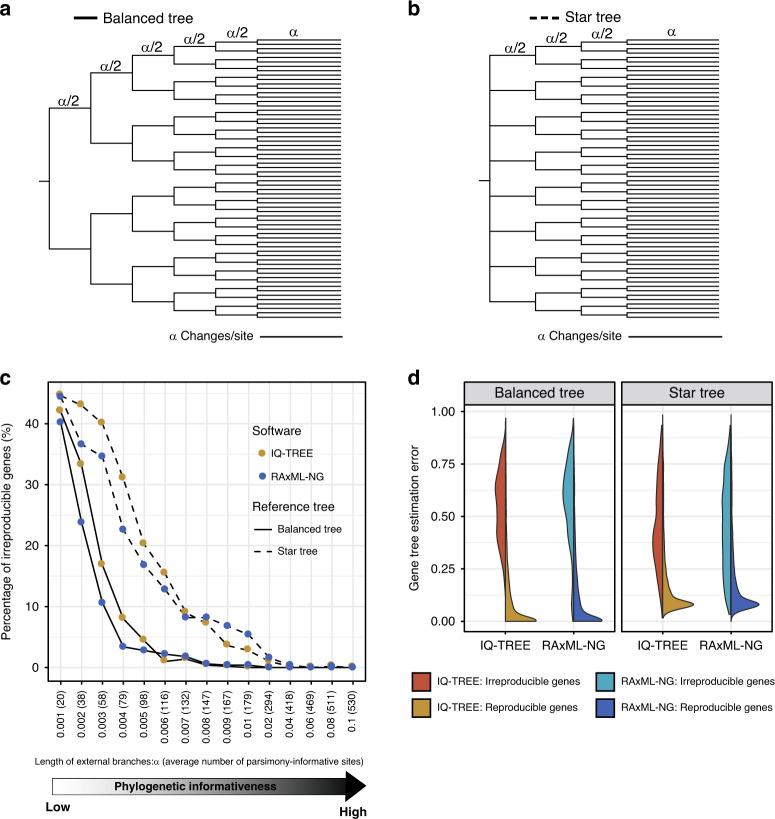
Fig. 6. The topologies of genes yielding irreproducible phylogenies are more likely to be incorrect than those of genes yielding reproducible phylogenies.
To examine whether genes yielding irreproducible phylogenies were more likely to be incorrect than genes yielding reproducible phylogenies, we simulated gene sequence alignments on 30 phylogenetic trees (15 balanced trees and 15 star trees with 64 taxa) that were scaled by branch length α (where α = 0.001, 0.002, 0.003, 0.004, 0.005, 0.006, 0.007, 0.008, 0.009, 0.01, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, or 0.1). Each phylogenetic tree was used to simulate 500 nucleotide sequence alignments, varying randomly in length from 300 to 1000 base pairs using Seq-Gen under the GTR model (-mGTR -a1 -g4 -i0 -f0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25 -n1 -or). For each of the 15,000 sequence alignments (30 phylogenetic trees * 500 sequence alignments), we assessed its reproducibility between two replicates (Run1 and Run2) on two separate nodes (i.e., each analysis was run on a single node, but Run1 was executed on a different node than Run2) using two threads on the CHTC cluster. a Balanced species tree of 64 taxa. Lengths of all external branches and internal branches are α and α/2, respectively. b The star species tree of 64 taxa is a balanced species tree with six zero-length internal branches near the root. c Percentage of genes that yielded irreproducible phylogenies plotted against α value of reference tree used in the simulation. d Comparison of gene tree estimation error between genes yielding irreproducible phylogenies and genes yielding reproducible phylogenies. Gene tree estimation error corresponds to the normalized Robinson–Foulds tree distance (nRFD) between the inferred tree and the reference tree. Genes yielding irreproducible phylogenies are colored in red and genes yielding reproducible phylogenies are colored in yellow when using IQ-TREE; genes yielding irreproducible phylogenies are colored in green and genes yielding reproducible phylogenies are colored in blue when using RAxML-NG. This comparison shows the genes that generate irreproducible phylogenies are more likely to be incorrect than genes that generate reproducible phylogenies. We observed a similar magnitude of gene tree estimation error (even though irreproducibility for IQ-TREE was two-fold higher) when using three threads per node. The 15 balanced trees, the 15 star trees, command lines, gene alignments, and gene trees, as well as statistics of the results, are available on the figshare repository: 10.6084/m9.figshare.11917770.