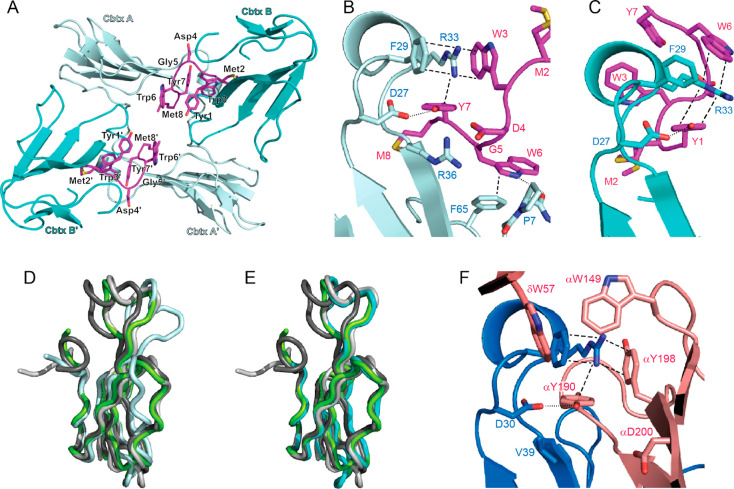
Figure 3.
Structure of the 12:α-Cbtx complex (PDB 6ZFM). (A) Asymmetric unit of the 12:α-Cbtx crystal structure. Each molecule of 12 (magenta) binds two toxin molecules A and B (light and dark cyan, respectively). A second α-Cbtx-A:12:α-Cbtx-B complex in the asymmetric unit is related by noncrystallographic symmetry. (B) Magnified view showing interaction of α-Cbtx loop II (light cyan) with 12 (magenta) in binding mode A. Two alternative conformations for the side chain of 12M2 were modeled. Key interacting amino acid residues shown in stick representation and labeled. Cation−π-stacking interactions and hydrogen bonds are highlighted by dashed and dotted lines, respectively. (C) Binding mode B, with second α-Cbtx molecule (dark cyan), from same structure with interacting residues drawn as in (B). (D) Binding mode A leads to conformational changes in α-Cbtx (light cyan) compared to the structure observed of α-Cbtx from Naja naja siamensis (dark gray, PDB 2CTX, root-mean-square deviation (rmsd) 1,31 Å), Naja naja oxania (light gray, PDB 1NTN, rmsd 1.7 Å), or Naja naja kaouthia in complex with AChBP (green, PDB 1YI5, rmsd 1.47 Å). The greatest displacement is observed in loop II (11 Å) and loop III (4.7 Å). (E) Binding mode B (cyan) resembles more closely previously reported structures of α-Cbtx from Naja naja siamensis (dark gray, rmsd 1,07 Å), Naja naja oxania (light gray, rmsd 0.67 Å), or Naja naja kaouthia in complex with AChBP (green, rmsd 0.87 Å). (F) Interaction of α-Bgtx (blue) loop II with the principal (α subunit) and complementary (δ subunit) faces of the muscle nAChR (pink, PDB 6UWZ). Key interacting residues drawn as in (B).