Figure 5.
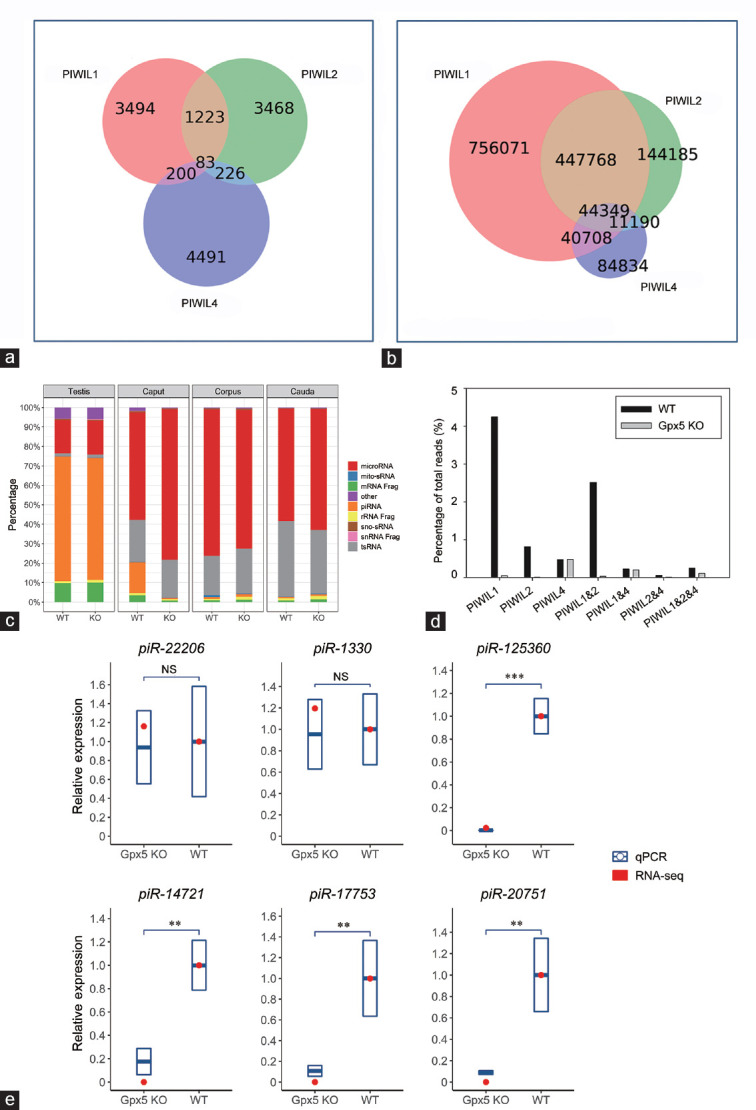
The piRNAs that potentially bind to PIWIL1 and PIWIL2, but not PIWIL4, were absent in the Gpx5-/- caput epididymidis. (a) The known PIWIL1-, PIWIL2-, and PIWIL4-binding piRNA data were, respectively, downloaded from previously published datasets GSM1565018, GSM475280, and GSM1220989. The top 5000 most abundant piRNAs in each dataset were selected to build a predefined list. The Venn diagram shows how these piRNAs overlap each other. (b) Potential interactions of the total piRNA reads of the 13-month-old caput epididymidis. (c) Profile of the sRNA constitution in the testis and different epididymal regions of WT and Gpx5-/- groups by RNA-seq. (d) Alteration of piRNAs that bind to different PIWI proteins in the 13-month-old Gpx5-/- caput epididymidis. (e) RT-qPCR validation of small RNA-seq data for six selected piRNAs in 13-month-old WT and Gpx5-/- mice. Quantitative PCR data are presented as means ± s.d. from three independent animals. NS: not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Student's t-test. The “snRNA Frag”, “rRNA Frag”, and “mRNA Frag” refer to the RNA fragments derived from snRNAs, rRNAs, and mRNAs, respectively. RT-qPCR: quantitative reverse transcription PCR; PIWI: P-element-induced wimpy testis; PIWIL1: piwi-like RNA-mediated gene silencing 1; PIWIL2: piwi-like RNA-mediated gene silencing 2; PIWIL4: piwi-like RNA-mediated gene silencing 4; s.d.: standard deviation; piRNA: PIWI-interacting RNA; snRNA: small nuclear RNA; sno-sRNA: small nuclear RNA-derived small RNA; mito-sRNA: mitochondrial RNA-derived small RNA; tsRNA: tRNA-derived small RNA.
