Figure 1.
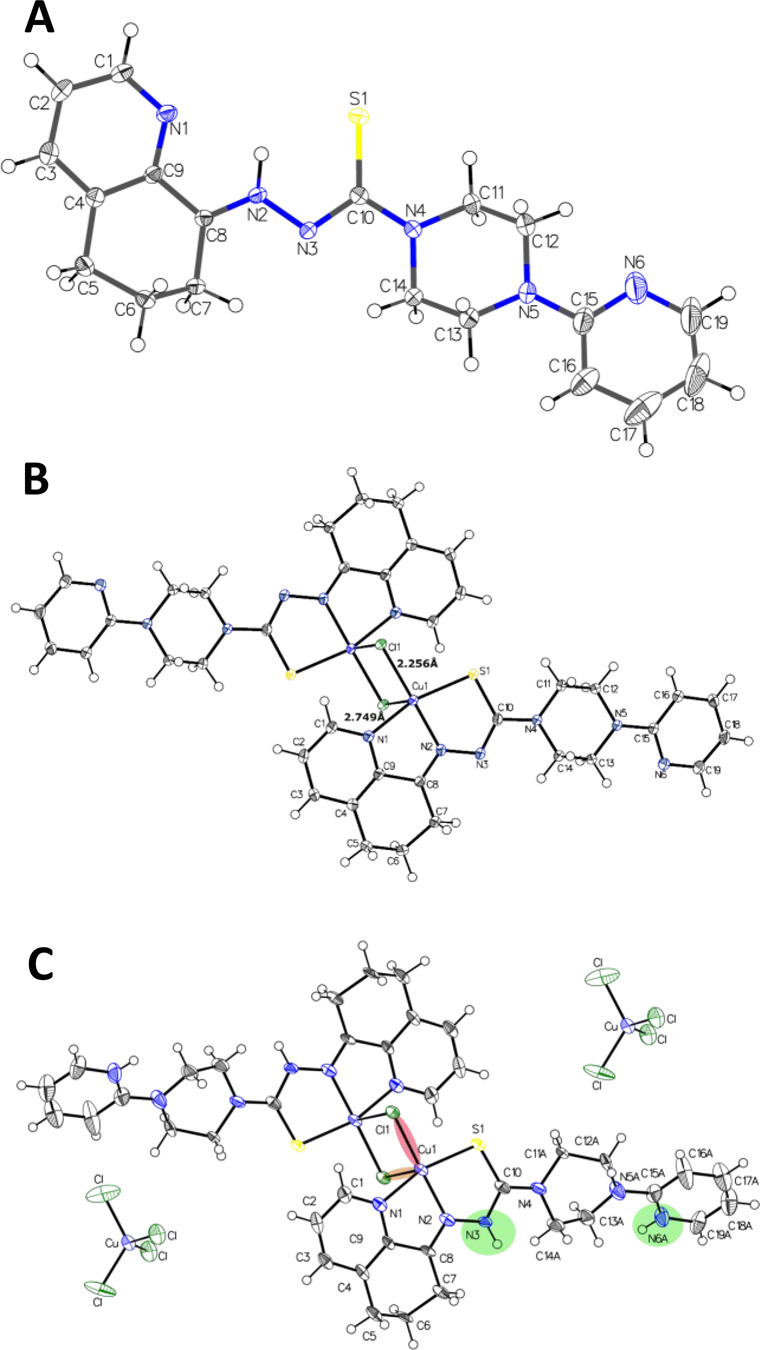
ORTEP plots of (A) COTI-2, (B) Cu-COTI-2a, and (C) Cu-COTI-2b with atom numbering. Ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. Selected bond lengths (Å) and bond angles (°) for (A) COTI-2 (bond precision for C–C single bond is 0.0030 Å): C8–N2 1.300(9), N2–N3 1.354(3), N3–C10 1.351(8), C10–S 1.717(1), C10–N4 1.361(4); N1–C9–C8 116.3, N2–N3–C10 112.0. For (B) Cu-COTI-2a (bond precision for C–C single bond is 0.0030 Å), two different types of Cu–Cl bonds occur: Cu1–Cl1 2.255(8) Å, Cu1–Cl1′ (1–X,–Y,–Z) 2.748(6) Å. Further selected bond lengths (Å) and bond angles (°): N1–Cu 2.029(9) Å, N2–Cu 1.961(3), S1–Cu 2.268(2) Å, Cu···Cu 3.52; Cl–Cu1–Cl′ 91.2, Cl–Cu–S 97.8, N1–Cu–N2 80.9, N2–Cu–S 84.2, N1–Cu1–Cl 96.3. For (C) Cu-COTI-2b (bond precision for C–C single bonds is 0.0121 Å), the main residue disorder is 39%. The counter ion [CuCl4]−2 position is shifted, and solvent (H2O) and the disordered second part were omitted for clarity. Two different types of Cu–Cl bonds occur: Cu1–Cl1 2.245(3) Å (light red shaded) and Cu1–Cl1′ (1–X,1–Y,1–Z) 2.719(8) Å (light orange shaded). Green-shaded areas visualize protonated nitrogen positions. Further selected bond lengths (Å) and bond angles (°): N1–Cu 2.022(7) Å, N2–Cu 1.958(8), S1–Cu 2.260(7) Å, Cu···Cu 3.42; Cl–Cu1–Cl′ 93.3, Cl–Cu–S 95.8, N1–Cu–N2 80.5, N2–Cu–S 84.8, N1–Cu1–Cl 98.1.
