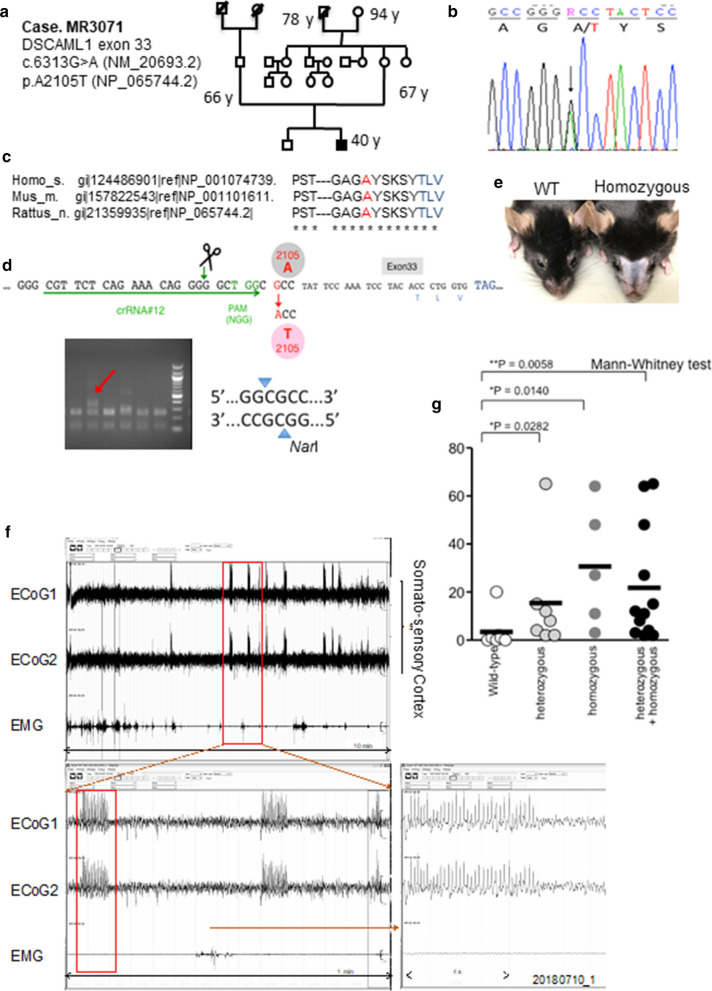
Fig. 6.
DSCAML1A2105T mutation of a patient with epilepsy and Dscaml1A2105T knock-in mice. a, b Pedigree and genomic sequence of the DSCAML1A2105T heterozygous patient. c Evolutionarily conserved c-terminal protein sequences of DSCAML1. d Generation of Dscaml1A2105T knock-in mice. Negative restriction enzyme (NarI) selection of heterozygous founder (red arrow). e Scratch-loss of hairs and whiskers in an adult male of Dscaml1A2105T/A2105T by hyper-grooming. f Representative ECoG of Dscaml1A2105T/A2105T mouse. g Numbers of epileptic spike-and-wave discharges in 6 h (n = 5–7, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Man-Whitney U-test, Error bars: s.e.m)