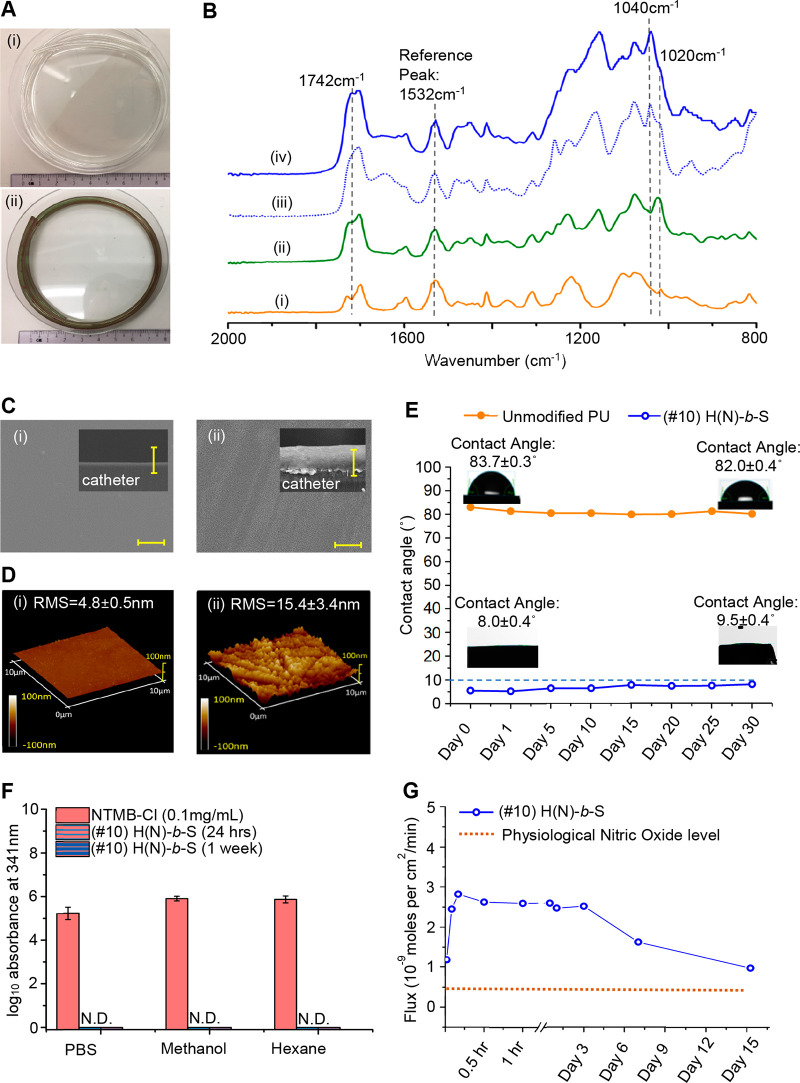
Figure 2.
Characterization of (#10) H(N)-b-S coating: (A) Visual appearance of long (i) (#1) unmodified and (ii) (#10) H(N)-b-S coated catheters. (B) FTIR-ATR characterization of steps in the synthesis of (#10) block copolymer coating: (i) unmodified PU control, (ii) first block of poly(HEMA), (iii) after second block copolymerization to make (#7) H-b-S, (iv) reaction of RSNO-Cl with subsurface poly(HEMA) block to get (#10) H(N)-b-S. (C) SEM characterizations (scale bar = 10 μm): surface and cross section (inset) of (i) (#1) unmodified PU and (ii) (#10) H(N)-b-S. (D) 3D AFM characterization of (i) unmodified PU catheter and (ii) (#10) H(N)-b-S. (E) Water contact angle change of (#10) H(N)-b-S over 1-month incubation in water. (F) HPLC detection of NO release precursor (NTMB-Cl) leaching to different solvents (N.D. refers to no detection of leaching). (G) NO release flux of (#10) H(N)-b-S coating at 37 °C over 15 days.