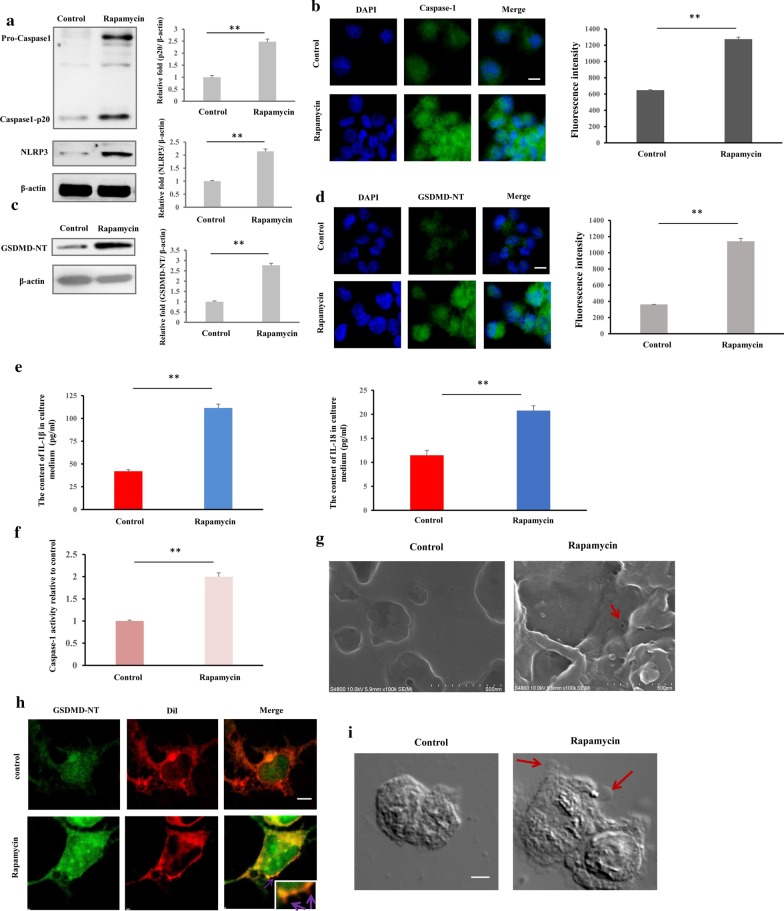
Fig. 4.
Rapamycin causes pyroptosis in macrophages. Macrophages were treated with rapamycin (100 nM) for 6 h, and the pyroptotic characteristics were examined. a Western blot of NLRP3 and caspase1-p20 expression. b Immunofluorescence assay of caspase 1 expression. Representative confocal microscopy images of caspase 1 expression (green) in cells that were co-stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars represent 10 μm. c Rapamycin upregulates GSDMD-NT expression. d Rapamycin upregulates GSDMD-NT expression in cells. Representative confocal microscopy images of caspase 1 expression (green) in cells that were co-stained with DAPI (blue) by immunofluorescence assay. Scale bars represent 10 μm. e Rapamycin increases the levels of IL-18 and IL-1β in cell culture medium. f Whole cell lysates were extracted from macrophages, Caspase-1 activity was determined by colorimetric assay and induced by rapamycin treatments. g Scanning electron microscopy of GSDMD-NT pores on plasma membrane in rapamycin-treated macrophages. Red arrow indicates GSDMD-NT pore. Scale bar, 500 nm. h GSDMD-NT (green) in cells co-stained with Dil (red) as membrane marker. Representative confocal microscopy images of rapamycin-treated macrophages and control cells by immunofluorescence assay. The purple arrows indicate the necks of budding vesicles in rapamycin-treated macrophages. Scale bars represent 1 μm. i Large bubbles by light microscopy, indicated by red arrows in pyroptotic cells. Scale bars represent 1 μm. The resolved bands were quantified using Gel-Pro Analyzer 4.0 (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD, USA). Fluorescence intensity of the immunofluorescent was measured by imaging analysis software (NIS-Elements Viewer, Nikon Instruments Inc. Shanghai, China). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. n = 3 independent experiments. Error bar indicates SD