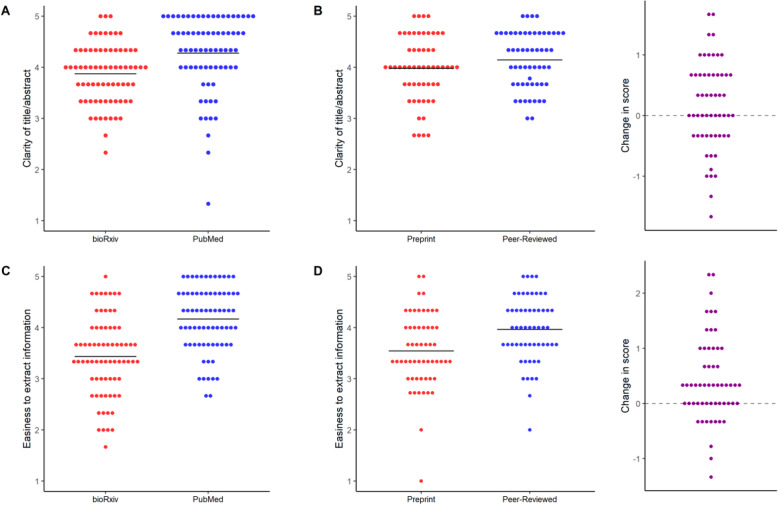
Fig. 6.
Subjective assessment by article source. a Clarity of title/abstract for the independent samples comparison. Scores were given as an answer to “Do the title and abstract provide a clear idea of the article’s main findings?”. Mean ± S.D.: bioRxiv = 3.9 ± 0.6, n = 72; PubMed = 4.3 ± 0.7, n = 72. 95% C.I. [0.2–0.6]. Student’s t-test: t = 3.61, p = 0.0004. b Clarity of title/abstract for the paired sample comparison. Mean ± S.D.: Preprint = 4.0 ± 0.6, n = 56; Peer-reviewed = 4.1 ± 0.5. 95% C.I. [− 0.03, 0.4]. Paired t-test: t = 1.66, p = 0.10. Right panel shows the differences between scores in preprint and peer-reviewed versions. c Easiness to extract information for the independent samples comparison. Scores were given as an answer to “Was the required information easy to find and extract from the article?”. Mean ± S.D.: bioRxiv = 3.4 ± 0.8, n = 72; PubMed = 4.2 ± 0.6. 95% C.I. [0.5, 1.0]. Student’s t-test: t = 6.22, p = 5.1 × 10− 9. d Easiness to extract information for the paired sample comparison. Mean ± S.D.: Preprint = 3.5 ± 0.7, n = 56; Peer-reviewed = 4.0 ± 0.6, n = 56. 95% C.I. [0.2, 0.6]. Paired t-test: t = 4.12, p = 0.0001. Right panel shows changes in score from preprint to peer-reviewed versions