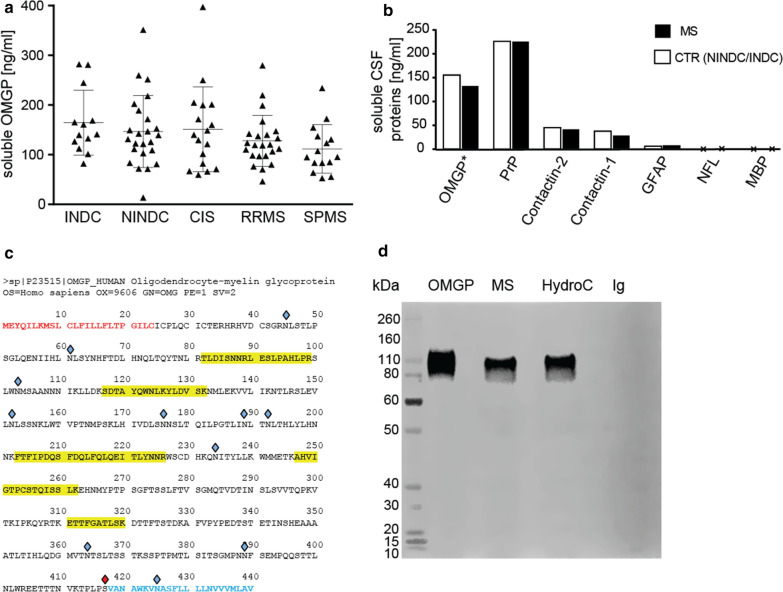
Fig. 3.
Soluble OMGP is abundant in the CSF. a Soluble OMGP was quantified in CSF from five cohorts of patients: inflammatory neurological disease control (INDC, n = 13), non inflammatory neurological disease control (NINDC, n = 24), clinically isolated syndrome (CIS, n = 17), relapsing–remitting MS (RRMS, n = 23) and secondary progressive MS (SPMS, n = 15). b Comparison of soluble OMGP to literature values of other soluble CSF proteins. Symbol (*) indicates that these data come from (a), displaying the mean of NINDC/INDC and RRMS cohorts, values for other proteins come from literature: PrP [47], Contactin and neurofilament light chain (NFL) [12], glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) [1] and myelin basic protein (MBP) [33]. c Sequence of human OMGP with identified peptides in CSF by mass spectrometry (LC-MSMS). Peptides are identified with a peptide false-discovery rate < 1% and are marked in yellow. The signal peptide is shown in red, the GPI anchor sequence in blue. Sites of glycosylation (according to Uniprot) are marked with blue diamonds; the GPI anchor site is marked with a red diamond. d Recombinant human OMGP (50 ng), pooled and 30-fold concentrated CSF from patients with MS or normal pressure hydrocephalus (HydrC), and 30 µg of human Ig (Ig) were loaded and separated by SDS-PAGE (full undigested gel), blotted and detected with polyclonal OMGP Ab (AF1674)