Fig. 2.
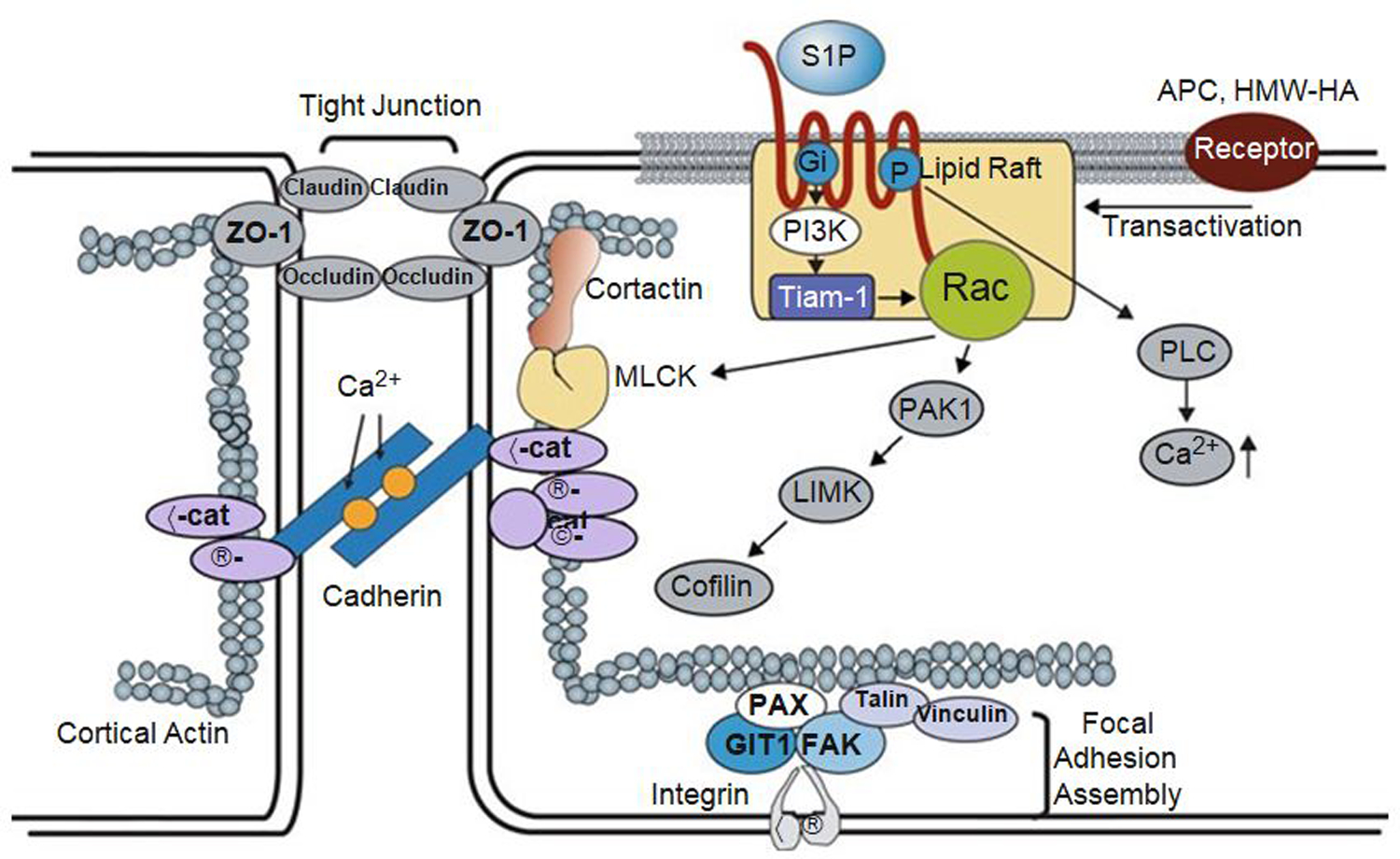
Regulation of vascular permeability by S1P/ SIP1 signaling. Binding of S1P to the SIP1 receptor stimulates the Gi-dependent recruitment of PI3 kinase, Tiam1, and Rac1 to lipid rafts (CEM), which serves to activate Rac1 in a Gi-PI3K-Tiam1-dependent manner. In addition, S1P induces an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration via a Gi-PLC pathway with additional activation of Rac1. After the activation of Rac1, S1P induces a series of profound events including adherens junction and tight junction assembly, cytoskeletal reorganization, and formation of focal adhesions that combine to enhance vascular barrier function. Furthermore, the transactivation of S1P1 signaling by other barrier-enhancing agents is recently recognized as a common mechanism for promoting endothelial barrier function. TJ tight junction, AJ adherens junction, S1P sphingosine-1-phosphate, SIP1 sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1, PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinase, Tiam 1 t-lymphoma invasion and metastasis gene 1, Rac1 Rho family of GTPase Rac1, PAK1 p21-activated protein kinase 1, LIMK LIM kinase, PLC phospholipase C, ZO-1 zona occluden protein-1, nmMLCK non-muscle myosin light-chain kinase, VE-Cad vascular endothelial cadherin, a-Cat a-Catenin, β-Cat β-Catenin, Vin vinculin, Pax paxillin, FAK focal adhesion kinase, GIT2 G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interactor-1, ECM extracellular matrix, APC activated protein C, HMW-HA high molecular weight hyaluronan [Modified from Wang and Dudek (2009)]
