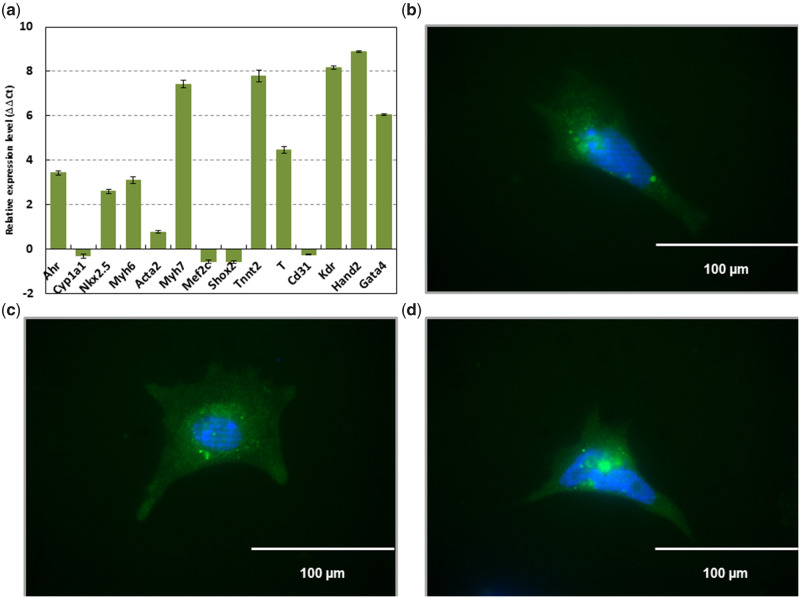
Figure 1.
Cells differentiated from mouse ES cells containing the plasmid pNkx2-5ProIRES2eGFP and selected for puromycin resistance express mesodermal markers characteristic of cardiomyocytes. RT-qPCR performed against Ahr (aryl hydrocarbon receptor), Cyp1a1 (cytochrome P450 1A1), Acta2 (actin alpha 2, smooth muscle), Gata4 (GATA-binding protein 4), Kdr (kinase insert domain protein receptor), Mef2c (myocyte enhancer factor 2C), Myh6 (myosin, heavy polypeptide 6, cardiac muscle, alpha), Myh7 (myosin, heavy polypeptide 7, cardiac muscle, beta), Nkx2.5 (NK2 homeobox 5), Shox2 (short stature homeobox 2), Tnnt2 (troponin T2, cardiac type), Cd31 (cluster of differentiation 31), Hand2 (heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2), and T (Brachyury) (A). Emission data were quantified using threshold cycle (Ct) values. Ct values for all genes analyzed were determined in biological duplicates or triplicates, and means were determined from the average Ct values for each biological duplicate. All means were normalized to Gapdh. The relative gene expression level to embryonic stem (ES) cells (ΔΔCt) was calculated as sample ΔCt (Ct of gene – Ct of Gapdh) relative to ES cell ΔCt (sample ΔCt – ES cell ΔCt). Immunofluorescence confirming eGFP driven by Nkx2-5 (B–D). Scale bar represents 100 µm at 40×.