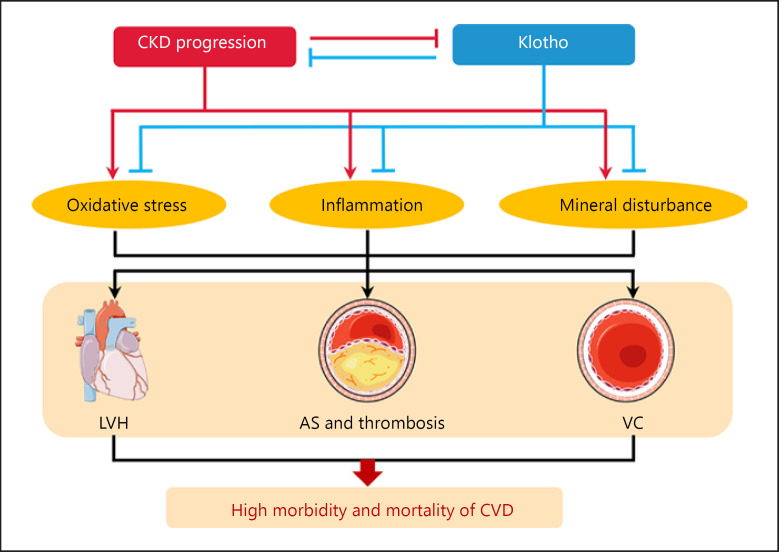
Fig. 1.
The role of Klotho in CKD-associated CVD. CKD is a public health epidemic. CVD, including uremic cardiomyopathy, vascular calcification, and atherosclerosis, was found in CKD subjects. Klotho deficiency, which results from renal insufficiency, is always associated with poor outcomes in CKD. By contrast, prevention of Klotho decline by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation as well as rectifying mineral disturbance can dramatically mitigate cardiac dysfunction, prevent vascular calcification, and retard the progression of CKD-accelerated atherosclerosis. AS, atherosclerosis; CVD, cardiovascular disease; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; VC, vascular calcification.