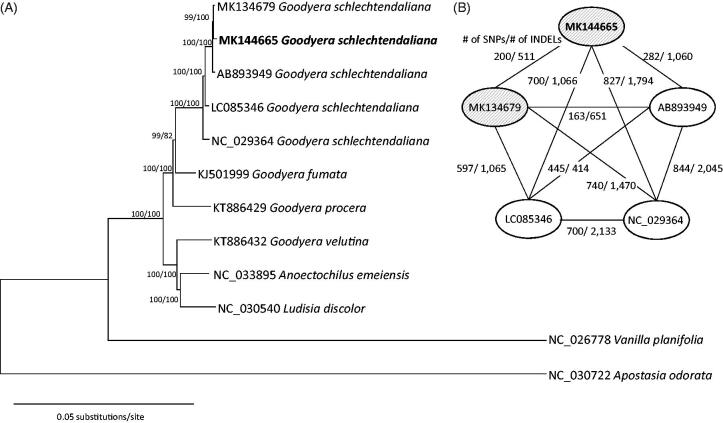
Figure 1.
(A) A maximum-likelihood tree using chloroplast genomes of G. schlechtendaliana from Korea (MK144665 in this study and MK134679) and previously published related taxa: G. schlechtendaliana from China (AB892949, LC085346, and NC_029364), G. fumata (KJ501999), G. procera (KT886429), G. velutina (KT886432), Ludisia discolour (NC_030540), Anoectochilus emeiensis (NC_033895), and two outgroup species, Vanila planifolia (NC_026778) and Apostasia odorata (NC_030722). Bootstrap values using the neighbor-joining and maximum-likelihood methods are indicated above the branch. (B) Pairwise comparisons of five chloroplast genomes of G. schlechtendaliana. Numbers of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions and deletions (INDELs) between each pair are indicate on the branch. Filled eclipses indicate G. schlechtendaliana originated from Korea and opened eclipses mean G. schlechtendaliana originated from China.