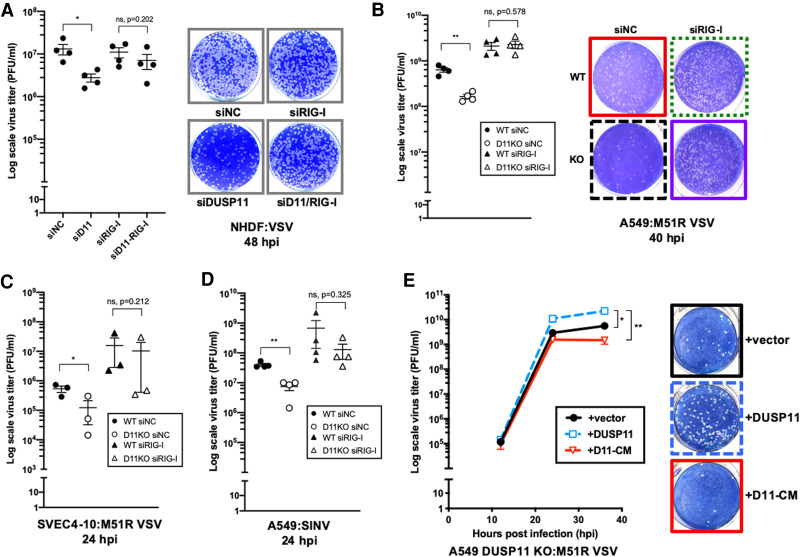
Figure 4.
DUSP11 catalytic activity promotes RNA virus replication. (A) VSV viral titer of negative control siRNA (siNC), siRNA targeting DUSP11 (siD11), or RIG-I (siRIG-I)-treated NHDF cells determined by plaque assay (left), and representative image of plaque assay of cells at 48 h postinfection (hpi) (right). Cells treated with siRNA were infected with WT VSV at MOI of 0.25 PFU/cell and virus supernatant was collected 48 hpi for plaque assay analysis. (B) M51R VSV viral titer of siNC or siRIG-I-treated A549 WT and DUSP11 KO cells determined by plaque assay (left), and representative image of plaque assay of cells at 40 hpi (right). Cells treated with siRNA were infected with M51R VSV at MOI of 0.05 PFU/cell. (C) M51R VSV viral titer of siNC or siRIG-I-treated SVEC4-10 WT and DUSP11 KO cells determined by plaque assay. Cells were infected with M51R VSV at MOI of 0.1 PFU/cell for 24 h. (D) SINV viral titer of siNC or siRIG-I-treated A549 WT and DUSP11 KO cells determined by plaque assay. Cells treated with siRNA were infected with SINV at MOI of 0.05 PFU/cell for 24 h. (E) M51R VSV viral titer of A549 DUSP11 knockout cells reconstituted with empty vector (vector), DUSP11 (DUSP11) or catalytic mutant DUSP11 (D11-CM) as in Figure 1A determined by plaque assay (left), and representative image of plaque assay of cells at 36 hpi (right). Cells were infected with M51R VSV at MOI of 0.05 PFU/cell and virus supernatant was collected 12, 24, and 36 hpi for plaque assay analysis. Data are derived from n = 4 independent replicates in A, B, and D), and n = 3 independent replicates in C and E. In all panels, data are presented as mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01 (two-tailed Student's t-test).