FIGURE 1.
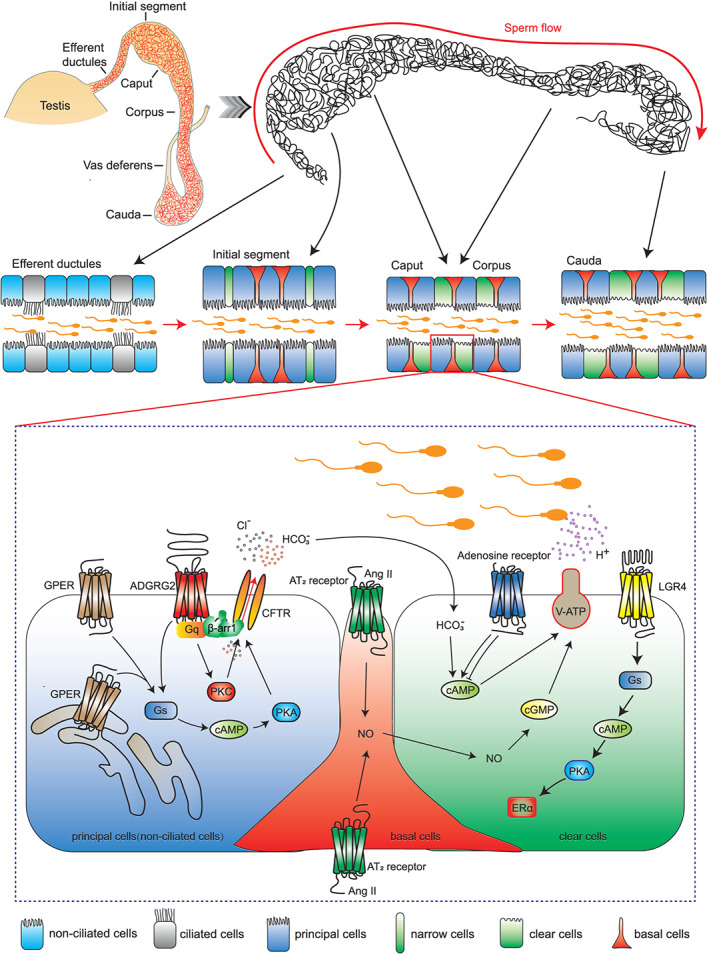
Diagram showing GPCR signalling and functions in the epididymis and efferent ductules. Above: The efferent ductules are a series of tubules that connect the rete testis to the epididymis. The epithelia of the efferent ductules are mainly composed of two cell types, ciliated cells and non‐ciliated cells. The epididymis is composed of one highly convoluted tubule. The epididymis is segmented morphologically and functionally into following distinct regions: the initial segment (not existing in human epididymis), the caput, the corpus, and the cauda. Each part consists of several cell types, including principal cells, narrow cells, clear cells, and basal cells. Inset: GPER activates cAMP‐CFTR‐chloride transportation to maintain the osmotic pressure of the perfusion solution. ADGRG2 is located exclusively on the apical membrane in non‐ciliated cells. ADGRG2/β‐arrestin1/Gq/CFTR forms a supercomplex that maintains pH and chloride anion homeostasis. AT2 receptors are specifically detected in basal cells and are essential for the proton‐secretion function of the epididymal lumen through activation of the NO‐cGMP pathway. Different members of the adenosine receptor family have opposite effects on the contractility of the epididymis. LGR4 activates Gs to increase intracellular cAMP levels, which promote ERα expression
