FIGURE 1.
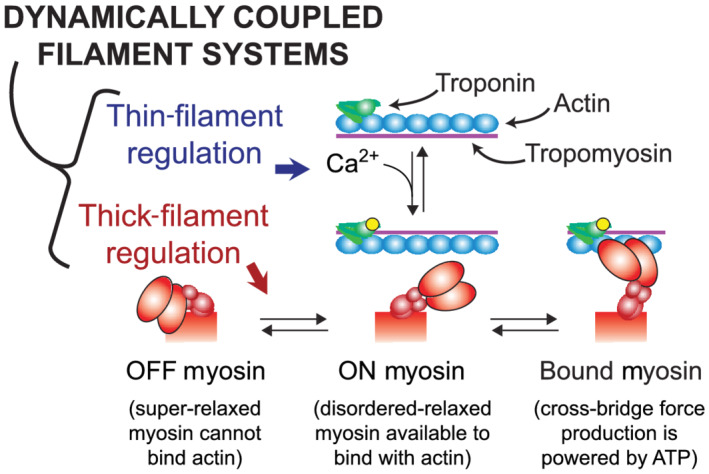
Schematic introducing dynamic filament coupling between thick and thin filaments. Thin‐filament regulation involves Ca2+ binding to troponin and subsequent movement of tropomyosin to expose actin sites along the thin filament, to which myosin can bind and form force‐generating cross‐bridges. Thick‐filament regulation involves myosin OFF–ON transition kinetics, which is a mechanosensitive equilibrium that shifts myosin heads from OFF to ON as muscle force increases. Myosin heads in the OFF state (also called the super‐relaxed state) cannot bind actin, whereas those in the ON state (also called the disordered‐relaxed state) can bind actin to form force‐generating cross‐bridges. This dynamic regulatory coupling implies that any modification to thin‐filament function will in turn change the status of thick‐filament regulation and vice versa (figure adapted from Campbell et al., 2018)
