FIGURE 1.
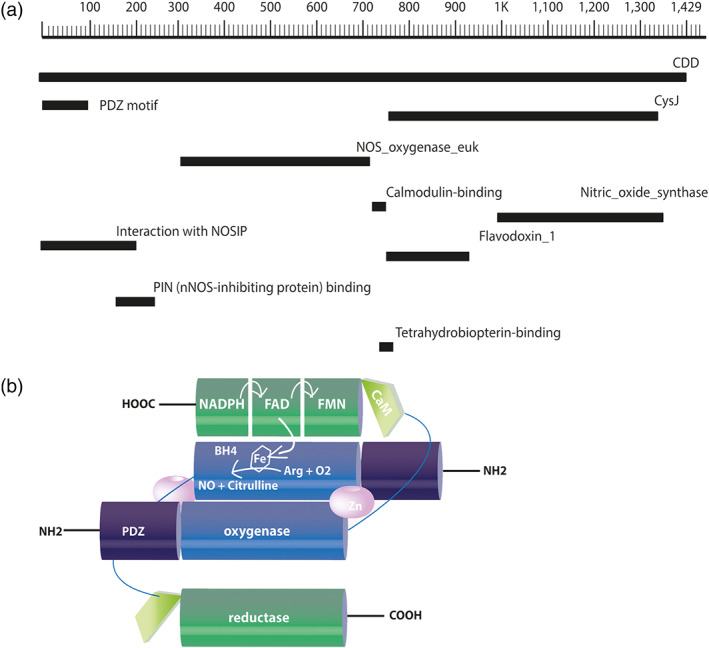
Schematic representation of the primary structure and the dimeric conformation of mouse neuronal NOS. (a) The primary structure of nNOS contains 1,434 amino acids in its chain and has a predicted molecular weight of 160.8 kDa. Amino acids are numbered in the form of a scale, and regions encoding structural domains and cofactor‐binding sites are shown in black bars according to their position on the chain of the nNOS. (b) The oxygenase/haem domain (blue) is connected to the reductase domain (green), consisting of the CysJ, flavodoxinJ, and ferrodoxin domains, by a flexible linker, containing a CaM‐binding sequence (light green). The FAD‐containing domain uses NADPH as an electron source. The FMN‐binding domain shuttles electrons from NADPH/FAD to the haem group of the oxygenase domain. The binding of CaM to NOS promotes the electron transfer from the FMN domain of one monomer to the haem domain of the other monomer. Arg, arginine; BH4, (6R)‐tetrahydrobiopterin; CaM, calmodulin; FAD, ferrodoxin; FMN, flavodoxin (flavin mononucleotide)
