Figure 4.
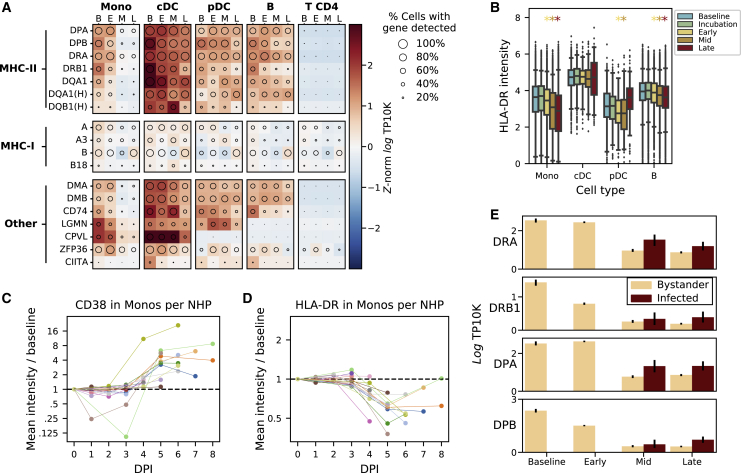
Monocytes Dramatically Reduce Expression of MHC Class II Proteins Independent of Infection Status
(A) Expression of major histocompatibility (MHC) or MHC-associated genes (rows) in key cell types at baseline (B), early (E), middle (M), or late (L) EVD (columns). Circle size: percentage of cells in that group in which the gene was detected; color: mean expression in Z score normalized, loge transcripts per 10,000 (TP10K). The “MAMU-” prefix, which designates MHC genes in rhesus monkeys, was removed; the “HLA-” prefix is indicated by “(H).”
(B) CyTOF intensity of HLA-DR protein in antigen-presenting cells. Boxes: median and interquartile range; whiskers: 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles. Colored stars indicate significant decreases from baseline (rank-sum test p < 0.05) with color corresponding to stage.
(C and D) Fold change (log2 scale) in average CD38 (C) and HLA-DR (D) CyTOF intensity on monocytes at each DPI relative to baseline, connected by colored lines for each NHP. See also Figure S4C and Data S1.
(E) Average gene expression (loge TP10K) for four MHC class II genes in monocytes, stratified by cell-infection status. Error bars: 95% CI on the mean based on 200 bootstraps.