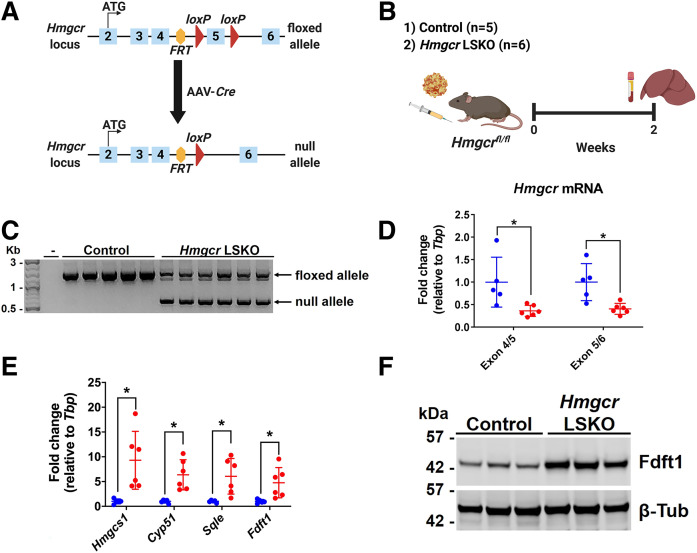
Fig. 1.
Efficient deletion of Hmgcr in the liver by AAV-Cre. A: Schematic diagram of genetic deletion of Hmgcr (exon 5) by AAV-Cre in the liver of Hmgcrfl/fl mice. B: Six-week-old Hmgcrfl/fl mice were injected with 2 × 1011 GCs of AAV-Cre or AAV-GFP (control). Two weeks postinjection, liver and plasma were collected for analyses. C: Genotyping PCR on liver DNA showing two main bands corresponding to the Hmgcr floxed (1,364 bp) and null (544 bp) alleles. Minus (-) indicates water only control. D: qPCR analysis of Hmgcr mRNA levels in livers from control (blue) and Hmgcr LSKO (red) mice. E: qPCR analysis of representative genes of the mevalonate pathway in the liver of Hmgcr LSKO (red) and control (blue) mice. F: Western blot analysis of Fdft1 in liver lysates from Hmgcr LSKO and control mice, with β-tubulin (β-Tub) used as a loading control. Hmgcs1, HMG-CoA synthase 1; Cyp51, cytochrome P450 family 51; Sqle, squalene epoxidase; Fdft1, farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1. Data are shown as mean ± SD with significance determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test (n = 5 control and 6 Hmgcr LSKO mice). *P < 0.05.