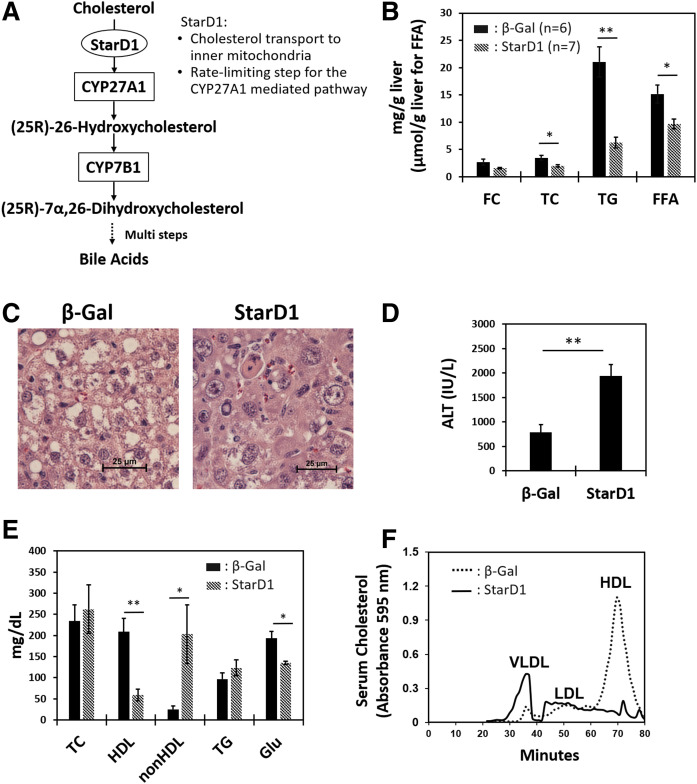
Fig. 1.
StarD1 overexpression leads to removal of cholesterol/lipids from livers of WD-fed B6/129 mice. StarD1 and β-Gal as control were overexpressed for the last 7 days in male mice fed a WD (Harlan-Teklad TD.88137) for 14 days. A: Key steps of the alternative pathway of bile acid synthesis in hepatocytes. B: StarD1 overexpression decreased liver TC, FC, FFA, and TG levels. C: Liver histology by H&E staining (40×) visually confirmed the measured biochemical reduction in liver lipid levels found with increased StarD1 expression. D: Increased ALT was observed in StarD1-overexpressed mice. E: Serum biochemical analysis revealed an increase in non-HDL (VLDL + LDL) level and a marked decrease in HDL and glucose (Glu). F: FPLC analysis demonstrated a marked increase in serum VLDL coupled to a dramatic decrease in the HDL fraction; findings consistent with serum biochemical analysis shown in panel E. β-Gal control, n = 6; StarD1 overexpression, n = 7. Welch’s t-tests were performed between β-Gal control and StarD1-overexpressed mice, and significance is indicated by *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001.