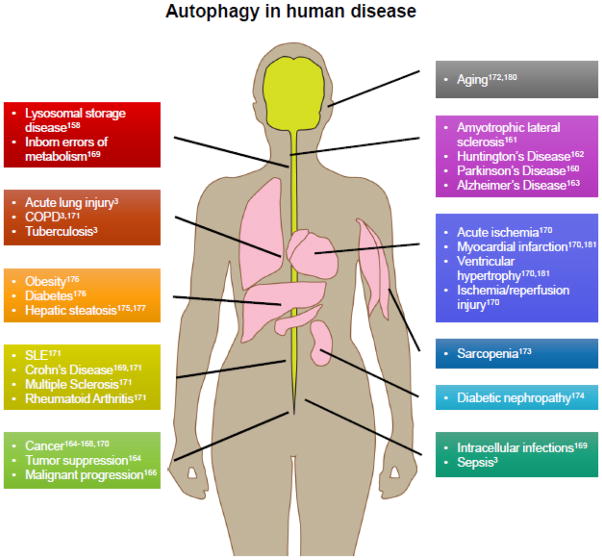
FIGURE 4. Autophagy in disease.
Aberrations in autophagy is implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases. Please refer to the cited references for more detailed treatments of autophagy and specific diseases. Autophagy is required for clearance of protein aggregates, dysfunctional organelles, and intracellular pathogens. Impaired autophagy is implicated in the severe neurologic phenotypes of congenital disorders as well as impaired clearance of invasive bacteria. Impaired autophagy is associated with aging and aging-associated diseases such as cancer, metabolic disorders, sarcopenia, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, and neurodegenerative conditions. Upregulated autophagy is a cell survival mechanism that is exploited in cancer increasing viability and resistance to chemotherapy, and is implicated in autoimmunity by promoting cell survival in lymphocytes in the face of apoptotic signaling.