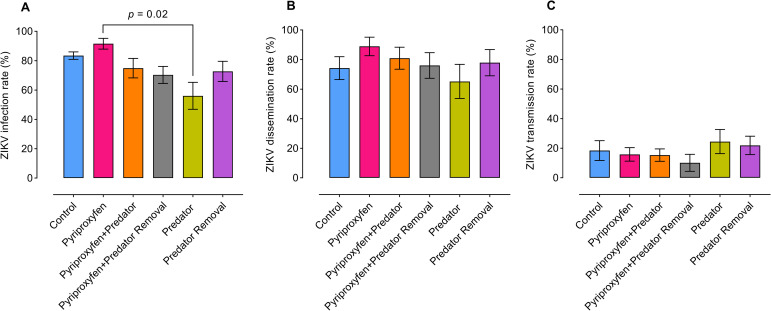
Fig 4. Effects of juvenile treatments on Ae. aegypti-ZIKV interactions.
(A) Zika virus infection, (B) disseminated infection, and (C) saliva infection (transmission) were determined following orally exposure to ZIKV infectious blood meals. Bars represent the means. Whiskers denote the standard error of the means. For all treatments, viral infection, disseminated infection, and transmission were estimated at 15 days post-ZIKV infection. Control (n = 80), pyriproxyfen (n = 50), pyriproxyfen+predator (n = 47), pyriproxyfen+predator removal (n = 64), predator (n = 49), and predator removal (n = 63). Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA.