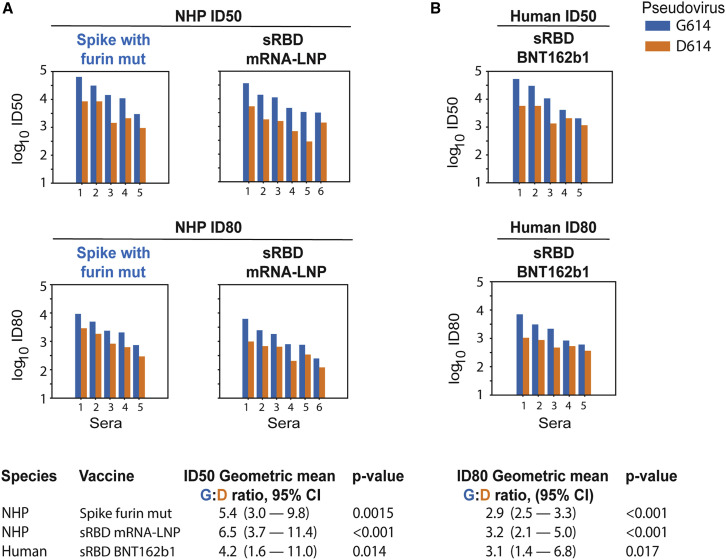
Figure 2.
The G614 Spike Is Neutralized More Potently than the D614 Spike by NHP Sera
The G614 spike is neutralized more potently than the D614 spike by sera from NHPs (rhesus macaques) immunized with nucleoside-modified mRNA-LNPs encoding RBD and full-length spike immunogens and humans immunized with RBD trimers. Sera from macaques immunized twice at a four-week interval with the Wuhan sequence of spike (D614) with a mutated furin cleavage site (n = 5) or secreted RBD monomers (n = 6) obtained four weeks after the second immunization were tested for neutralization against pseudoviruses with the D614 and G614 variants of spike (A). Also shown are sera from five humans immunized twice at a three-week interval with nucleoside-modified mRNA-LNPs encoding a secreted RBD trimer (B). Each pair of bars represents one macaque or human. Top panels are ID50; bottom panels are ID80. For each serum, the blue bar shows the neutralization sensitivity of the G614 form, and the orange bar shows the original D614 form. The geometric means for the ratio of G614:D614 neutralizing antibody titers measured in sera are provided in the summary at the bottom. Log10 of values of the ID50 and ID80 titers were used in a paired t test to calculate the p value and the 95% CI of geometric mean for the ratio of G614:D614. Overall response levels were comparable between the two different immunogens in the NHP and between NHPs and humans.