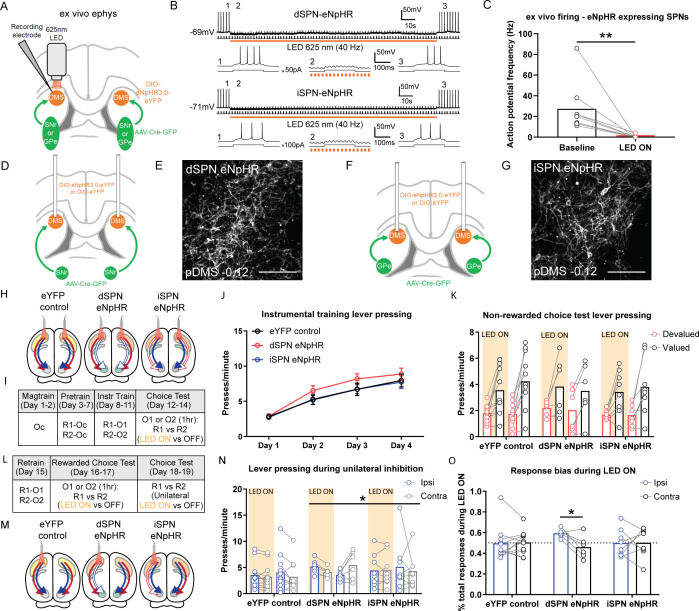
Figure 4. Bilateral optogenetic inhibition of direct spiny projection neurons (dSPNs) or indirect spiny projection neurons (iSPNs) leaves the expression of goal-directed learning intact but unilateral inhibition of dSPNs biases performance.
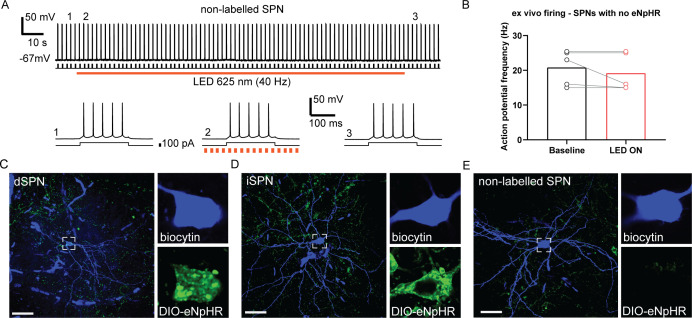
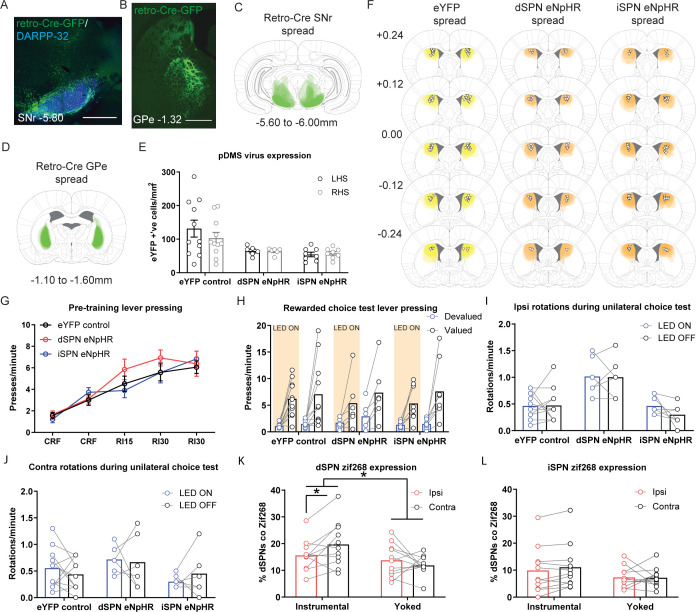
(A) Schematic depicting the design for ex vivo recordings; retro-Cre was injected into the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) or globus pallidus (GPe) and DIO-eNpHR into the posterior dorsomedial striatum (pDMS); direction of arrows indicates retrograde transport of the virus. (B) Example trace from one dSPN (top) and iSPN (bottom) expressing eNpHR recorded under current-clamp with an injection of +50 or +100 pA current (200 ms, 0.5 Hz). Orange bar denotes time period when 625 nm LED was applied to the neuron (40 Hz, 150 s). Bottom three panels of each SPN are expanded traces from the above at time points before (1), during (2), and after (3) LED illumination. (C) Action potential frequency of eNpHR-labelled SPNs (four dSPNs and five iSPNs) at baseline (10 s period before LED) versus LED (10 s period from beginning of LED). (D) Surgery design for targeting dSPNs; retro-Cre was injected bilaterally into the SNr and DIO-eNpHR or DIO-eYFP was injected bilaterally into the pDMS. Cannulae were inserted bilaterally into the pDMS. (E) Confocal image (scale bar, 100 µm) showing DIO-eNpHR expression in pDMS dSPNs. (F and G) Same as D and E but for pDMS iSPNs; retro-Cre was injected into the GPe. (H) Summary of experimental groups; blue arrows indicate intact direct pathway, red arrows indicate intact indirect pathway, and unfilled arrows indicate inhibited pathway. (I) Summary of the experimental design; R1 and R2 indicate left and right lever responses; Oc, O1, and O2 indicate distinct food outcomes; LED ON versus OFF indicates training or test days when LED light was delivered. (J) Mean (± SEM) lever presses per minute averaged across each day of instrumental training for each group. (K) Mean presses per minute on the devalued and valued lever for each rat in each group, averaged across two tests, during LED ON (orange shaded) and LED OFF (non-shaded) periods. (L) Continuation of I. (M) Same as H but showing unilateral LED manipulation. (N) Mean presses per minute on the lever ipsilateral and contralateral to unilateral inhibition for each rat in each group during periods of LED ON (orange shaded) and LED OFF (non-shaded), averaged across two tests with inhibition in each hemisphere. (O) Mean proportion of responding on the ipsilateral and contralateral lever during the LED ON period, as a proportion of the total responding on each respective lever, for each animal in each group, averaged across two tests. For all data, bars represent group means. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.