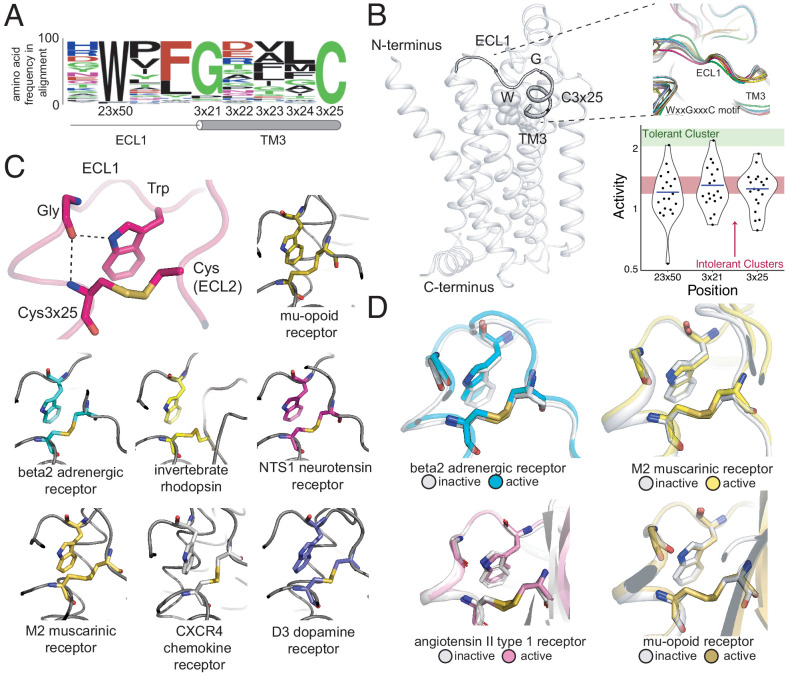
Figure 6. A conserved extracellular tryptophan-disulfide ‘structural latch’ in class A GPCRs is mutationally intolerant and conformation-independent.
(A) Sequence conservation of extracellular loop 1 (ECL1) and the extracellular interface of TM3 (202 Class A GPCRs with a disulfide bridge between TM3 and ECL1). (B) Left: Depiction of the interaction of W9923x50, G1023x21, and C1063x25 in ECL1 of the β2AR. Top Right: Conservation of the structure of the ECL1 region across functionally different class A GPCRs. Bottom Right: Activity of all 19 missense variants assayed for each of the three conserved residues, with the mean activity (mutational tolerance) shown as a blue bar. The shaded bars represent the mean mutational tolerance ± 1 SD of residues in the tolerant Cluster 6 (green) and the intolerant Clusters 1 and 2 (red). (C) A hydrogen bond network between mutationally intolerant positions W9923x50, G1023x21, and C1063x25. Representative examples of the structural latch are shown. (D) This structural latch is maintained in both the inactive and active state structures for the β2AR (inactive: 2RH1, active: 3P0G), the M2 muscarinic receptor (inactive: 3UON, active: 4MQS), the angiotensin II type one receptor (inactive: 4ZUD, active: 6OS1), and the mu-opioid receptor (inactive: 4DKL, active: 5C1M).